Aquaponics vs hydroponics: two innovative farming methods that have captivated the attention of the agricultural world. As we delve into this captivating topic, we will explore the unique characteristics, advantages, and applications of each system, leaving you with a comprehensive understanding of their transformative potential.
From the fusion of aquaculture and hydroponics in aquaponics to the controlled environment of hydroponics, this journey will illuminate the intricacies of these sustainable farming practices, empowering you to make informed decisions about the future of food production.
Overview
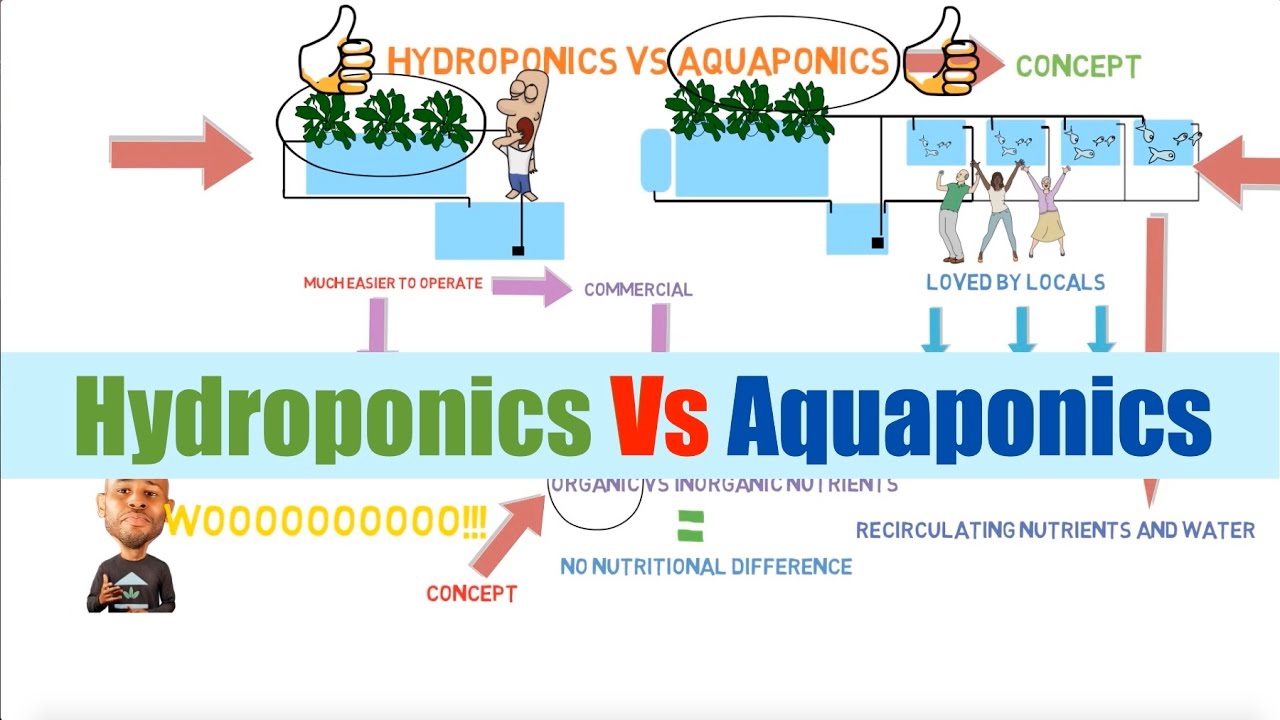
Aquaponics and hydroponics are both soilless gardening techniques that have gained popularity in recent years. Both systems offer advantages over traditional soil-based gardening, but they also have their own unique characteristics and requirements.
Aquaponics is a combination of aquaculture (the raising of fish) and hydroponics (the growing of plants in water). In an aquaponics system, the fish waste provides nutrients for the plants, and the plants help to clean the water for the fish.
This creates a closed-loop system that is both efficient and sustainable.
Hydroponics, on the other hand, is the growing of plants in water that is enriched with nutrients. Hydroponic systems can be either open or closed. In an open system, the nutrient-rich water is constantly flushed away and replaced with fresh water.
In a closed system, the nutrient-rich water is recirculated and reused.
Comparison of Aquaponics and Hydroponics
The following table compares the key differences between aquaponics and hydroponics:
| Feature | Aquaponics | Hydroponics |
|---|---|---|
| Water source | Fish tank water | Nutrient-rich water |
| Nutrient source | Fish waste | Added nutrients |
| System type | Closed-loop | Open or closed |
| Plant growth | Typically slower than in hydroponics | Typically faster than in aquaponics |
| Fish production | Yes | No |
Aquaponics
Aquaponics is a food production system that combines aquaculture (the raising of fish) and hydroponics (the growing of plants in water). Aquaponics systems use the waste from fish to fertilize the plants, and the plants help to clean the water for the fish.
This creates a symbiotic relationship between the two organisms, and it can be a very efficient way to produce food.
Components of an Aquaponics System
The main components of an aquaponics system are the fish tank, the grow bed, the water pump, and the filter. The fish tank is where the fish are raised. The grow bed is where the plants are grown. The water pump circulates the water between the fish tank and the grow bed.
The filter removes solids from the water.
Benefits of Aquaponics, Aquaponics vs hydroponics
There are many benefits to using aquaponics, including:
- Environmental sustainability:Aquaponics systems are very efficient in their use of water and nutrients. They also produce less waste than traditional agriculture methods.
- Economic efficiency:Aquaponics systems can be very profitable, as they can produce both fish and plants. They can also be used to grow a variety of crops, which can help to reduce the risk of crop failure.
- Nutritional value:Fish and plants grown in aquaponics systems are typically very high in nutrients. This is because the fish waste provides a constant source of nutrients for the plants.
Examples of Successful Aquaponics Operations
There are many successful aquaponics operations around the world. One example is the Nelson and Pade Aquaponics farm in California. This farm produces over 100,000 pounds of fish and vegetables each year. Another example is the Urban Organics aquaponics farm in Chicago.
This farm produces over 10,000 pounds of fish and vegetables each year, and it is located in a densely populated urban area.
Hydroponics

Hydroponics is a method of growing plants in a water-based, nutrient-rich solution. It is a popular choice for commercial growers and home gardeners alike, as it offers a number of advantages over traditional soil-based gardening.Hydroponic systems can be divided into two main types:
- Open systems: In open systems, the nutrient solution is not recirculated and is simply discarded after use. This type of system is less expensive to set up and maintain, but it is also less efficient than closed systems.
- Closed systems: In closed systems, the nutrient solution is recirculated and reused. This type of system is more expensive to set up and maintain, but it is also more efficient and can result in higher yields.
There are a number of advantages to using hydroponics over traditional soil-based gardening, including:
- Increased yields: Hydroponic systems can produce higher yields than soil-based gardens because they provide plants with a constant supply of nutrients and water.
- Faster growth: Plants grown in hydroponic systems typically grow faster than plants grown in soil because they have access to a constant supply of nutrients and water.
- Reduced water usage: Hydroponic systems use up to 90% less water than traditional soil-based gardens.
- Reduced fertilizer usage: Hydroponic systems use up to 50% less fertilizer than traditional soil-based gardens.
- No need for soil: Hydroponic systems do not require soil, which can save money and time.
However, there are also some disadvantages to using hydroponics, including:
- Higher initial cost: Hydroponic systems can be more expensive to set up than traditional soil-based gardens.
- More maintenance: Hydroponic systems require more maintenance than traditional soil-based gardens, as the nutrient solution must be monitored and adjusted regularly.
- Risk of disease: Hydroponic systems can be more susceptible to disease than traditional soil-based gardens because the plants are grown in a water-based environment.
Overall, hydroponics is a viable alternative to traditional soil-based gardening that offers a number of advantages. However, it is important to weigh the advantages and disadvantages carefully before deciding whether or not to use hydroponics. Examples of successful hydroponic operationsThere are a number of successful hydroponic operations around the world.
Some of the most notable include:
- Green Sense Farms: Green Sense Farms is a large-scale hydroponic operation in the Netherlands that produces over 1 million pounds of tomatoes per year.
- Gotham Greens: Gotham Greens is a rooftop hydroponic farm in New York City that produces over 1 million pounds of leafy greens per year.
- Bright Farms: Bright Farms is a hydroponic farm in Chicago that produces over 1 million pounds of leafy greens and herbs per year.
These are just a few examples of the many successful hydroponic operations around the world. Hydroponics is a growing industry, and it is likely that we will see even more successful hydroponic operations in the years to come.
Comparison of Aquaponics and Hydroponics

Aquaponics and hydroponics are two closely related plant cultivation systems that use water as the primary growing medium. However, there are some key differences between the two systems.
Aquaponics is a system that combines aquaculture (the raising of fish) with hydroponics (the growing of plants in water). In an aquaponics system, the fish waste provides nutrients for the plants, and the plants help to clean the water for the fish.
Hydroponics, on the other hand, is a system that uses only water and nutrients to grow plants. There are no fish involved in a hydroponics system.
Similarities and Differences
Both aquaponics and hydroponics offer a number of advantages over traditional soil-based gardening, including:
- Increased yields: Plants grown in water can absorb nutrients more easily than plants grown in soil, which leads to increased yields.
- Reduced water usage: Aquaponics and hydroponics use significantly less water than traditional soil-based gardening.
- Reduced labor costs: Aquaponics and hydroponics require less labor than traditional soil-based gardening, as there is no need to till, weed, or water the plants.
However, there are also some differences between the two systems.
- Startup costs:Aquaponics systems can be more expensive to set up than hydroponics systems, as they require both a fish tank and a hydroponics system.
- Maintenance:Aquaponics systems require more maintenance than hydroponics systems, as they need to be monitored for water quality and fish health.
- Space requirements:Aquaponics systems require more space than hydroponics systems, as they need to accommodate both a fish tank and a hydroponics system.
Yields, Costs, and Environmental Impact
The yields of aquaponics and hydroponics systems can vary depending on the type of plants being grown and the size of the system. However, in general, aquaponics systems can produce higher yields than hydroponics systems, as the fish waste provides additional nutrients for the plants.
The costs of aquaponics and hydroponics systems can also vary depending on the size and complexity of the system. However, in general, hydroponics systems are less expensive to set up and maintain than aquaponics systems.
The environmental impact of aquaponics and hydroponics systems is also different. Aquaponics systems are more environmentally friendly than hydroponics systems, as they recycle fish waste and use less water.
Advantages and Disadvantages
The following table summarizes the key advantages and disadvantages of aquaponics and hydroponics systems:
| Aquaponics | Hydroponics | |
|---|---|---|
| Advantages | – Higher yields
|
– Less expensive to set up and maintain
|
| Disadvantages | – More expensive to set up
|
– Lower yields
|
Applications

Aquaponics and hydroponics find applications in various settings, depending on their suitability for different crop types and environmental conditions.
While both aquaponics and hydroponics involve growing plants in water, aquaponics has the added benefit of integrating fish farming. If you’re considering setting up an aquaponics system, it’s important to plan your design carefully. You’ll need to consider the size of your system, the type of fish you want to raise, and the plants you want to grow.
You can find helpful information on aquaponics setup design online. With proper planning, you can create a successful aquaponics system that will provide you with fresh fish and vegetables for years to come. And unlike hydroponics, aquaponics mimics a natural ecosystem, making it a more sustainable option.
Aquaponics is particularly suited for growing leafy greens, herbs, and fish, as it provides a symbiotic relationship between plants and fish. Hydroponics, on the other hand, is more versatile and can be used to grow a wider range of crops, including fruits, vegetables, and flowers.
Suitability for Different Crops and Environments
- Aquaponics:Best suited for leafy greens, herbs, and fish in controlled environments (e.g., greenhouses, indoor facilities).
- Hydroponics:Can grow a wider range of crops, including fruits, vegetables, and flowers, in both controlled and uncontrolled environments (e.g., greenhouses, vertical farms, outdoor systems).
Innovative Uses
- Aquaponics:Used in urban farming, rooftop gardens, and community-supported agriculture (CSA) programs.
- Hydroponics:Employed in space exploration, disaster relief, and remote locations with limited access to soil and water.
Future Trends: Aquaponics Vs Hydroponics
Aquaponics and hydroponics are rapidly evolving fields, driven by technological advancements and growing awareness of their potential to address global food security and environmental challenges.
Emerging trends in these systems include:
Integration of Artificial Intelligence
- AI-powered monitoring and control systems optimize water quality, nutrient levels, and plant growth conditions.
- Predictive analytics forecast crop yields, identify potential problems, and suggest corrective actions.
Vertical Farming
- Vertical farms maximize space utilization, allowing for increased crop production in urban areas.
- Controlled environments ensure optimal growing conditions and minimize environmental impact.
Hybrid Systems
- Combining aquaponics and hydroponics creates synergistic systems that benefit both plants and fish.
- Hydroponically grown plants provide nutrients to the fish, while the fish waste fertilizes the plants.
Nutrient Recovery and Water Conservation
- Advanced filtration and water treatment technologies recover nutrients from wastewater, reducing environmental pollution.
- Water-efficient irrigation systems minimize water consumption and promote sustainable water management.
Research and Development
- Ongoing research focuses on improving plant varieties, optimizing nutrient delivery systems, and developing disease-resistant crops.
- Collaboration between scientists, engineers, and farmers drives innovation and advances the field.
Final Wrap-Up
In the realm of sustainable farming, aquaponics and hydroponics stand as beacons of innovation, offering solutions to the challenges of food security and environmental conservation. Whether you are a seasoned farmer or simply curious about the future of agriculture, this exploration has provided valuable insights into the potential of these systems to shape a more sustainable and prosperous world.
FAQ
What is the key difference between aquaponics and hydroponics?
Aquaponics integrates fish farming with plant cultivation, while hydroponics solely focuses on growing plants in a nutrient-rich water solution.
Which system is more suitable for small-scale operations?
Hydroponics is generally more accessible for small-scale growers due to its lower space and water requirements.
Can aquaponics be used to grow a wide variety of crops?
Yes, aquaponics can support a diverse range of plants, including leafy greens, herbs, fruits, and vegetables.
