Step by Step Aquaponics: Embark on a journey of sustainable food production, combining the principles of aquaculture and hydroponics to create a thriving ecosystem in your backyard.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of aquaponics, providing you with the knowledge and practical steps to establish a thriving system. From selecting the right components to maintaining optimal water quality, we will guide you through every aspect of aquaponics, empowering you to cultivate healthy plants and fish in harmony.
System Overview
Aquaponics is an innovative system that seamlessly combines aquaculture (fish farming) and hydroponics (plant cultivation). It’s a sustainable and resource-efficient method that offers numerous advantages.
The fundamental concept behind aquaponics is the integration of these two disciplines, where the water from fish tanks is utilized to nourish plants grown hydroponically. This nutrient-rich water provides an ideal growth medium for plants, eliminating the need for chemical fertilizers.
Benefits of Aquaponics
- Water Conservation:Aquaponics significantly reduces water consumption compared to traditional farming methods. The water used in fish tanks is recirculated and reused for plant growth, minimizing water wastage.
- Reduced Fertilizer Usage:The fish waste provides a natural source of nutrients for plants, eliminating the need for synthetic fertilizers. This not only reduces costs but also promotes organic farming practices.
- Increased Crop Yields:The nutrient-rich water from fish tanks enhances plant growth and yields. Aquaponic systems have been shown to produce higher crop yields compared to traditional soil-based farming methods.
Components of an Aquaponics System
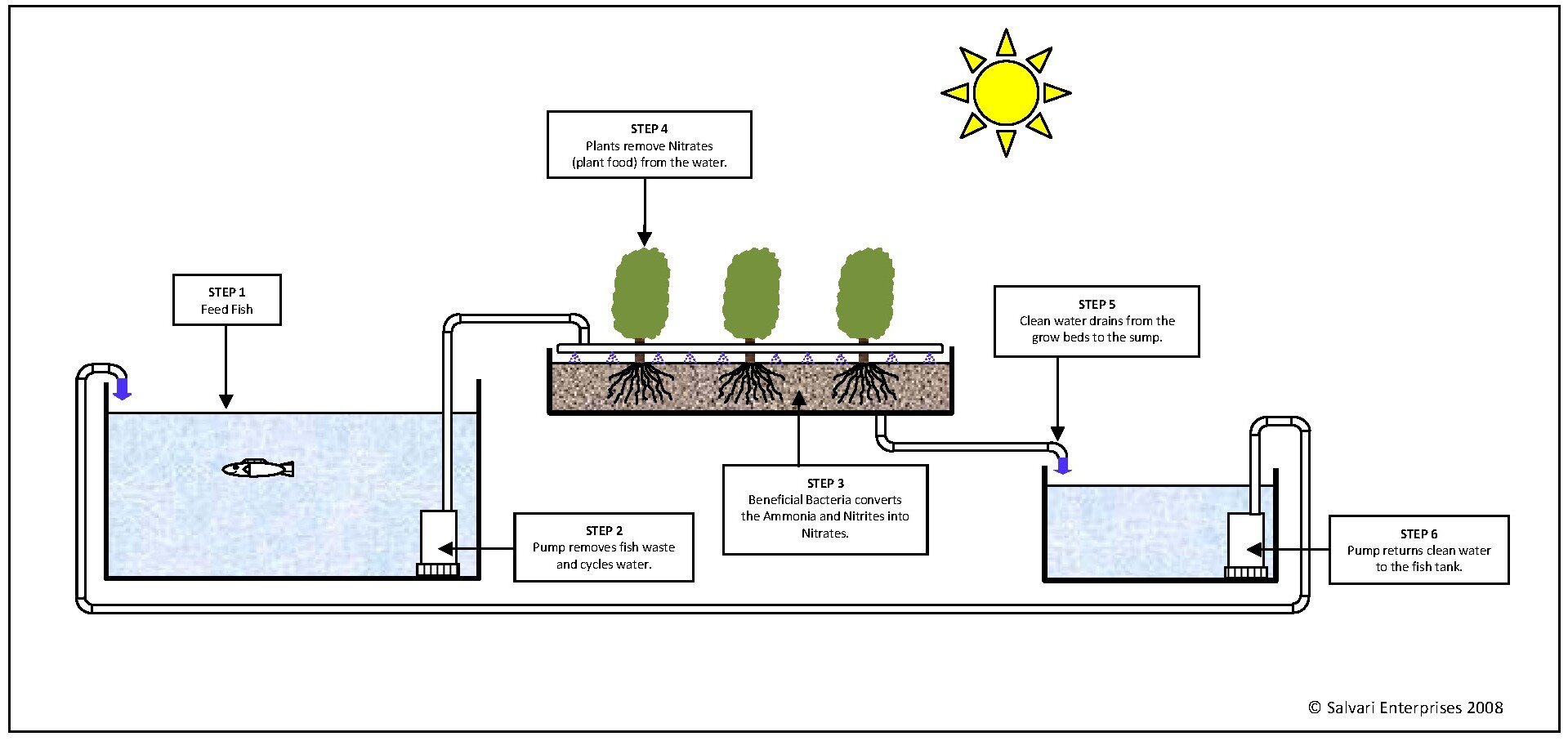
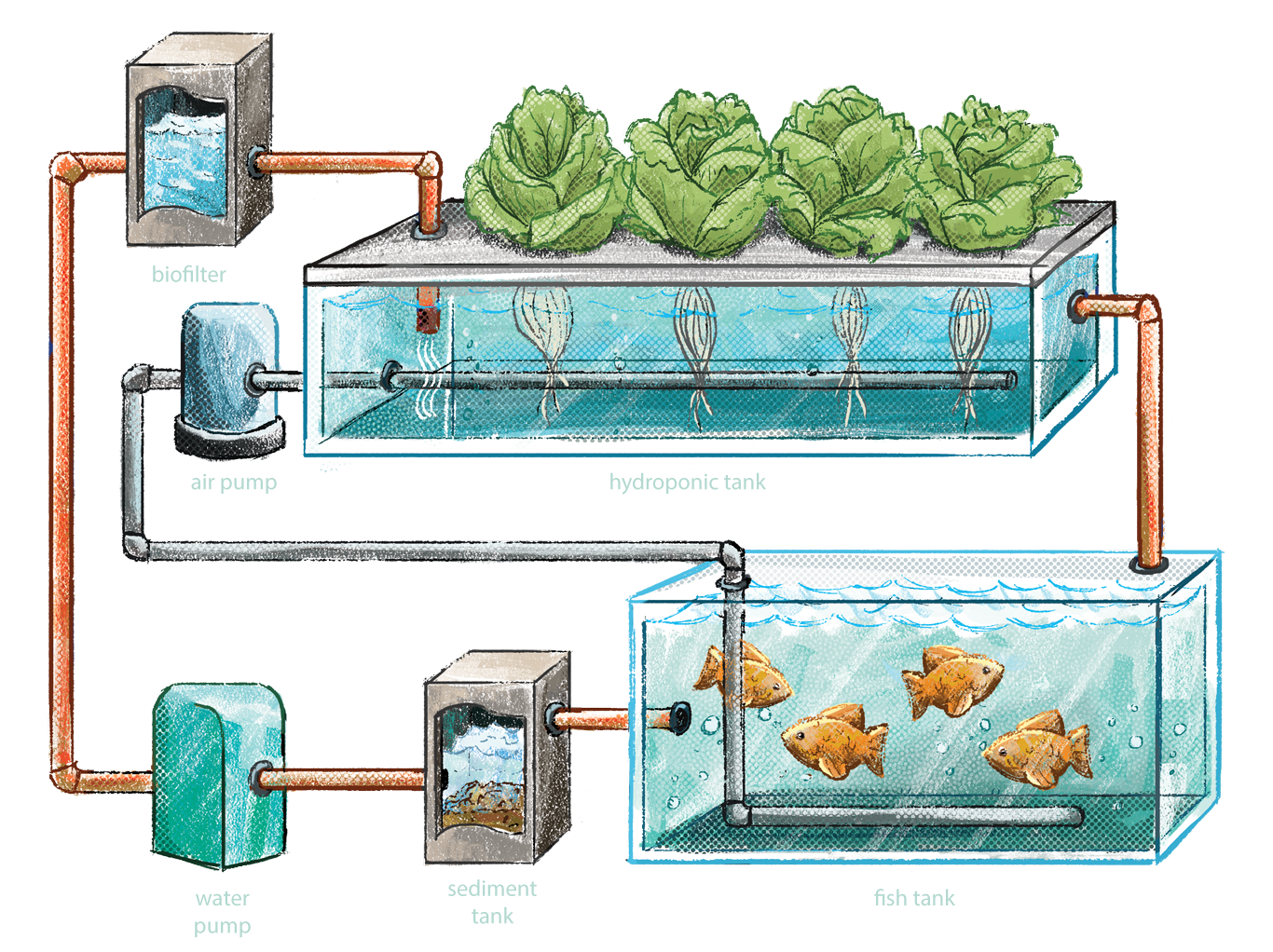
An aquaponics system comprises several interconnected components that work together to create a thriving ecosystem for both fish and plants. These components include a fish tank, grow beds, a water pump, and a filtration system.
Fish Tank
- Houses the fish, providing them with a suitable environment to live and thrive.
- The water in the fish tank contains fish waste, which is a rich source of nutrients for plants.
Grow Beds
- Contain the plants and provide a medium for their growth.
- The water from the fish tank, rich in nutrients, is pumped into the grow beds, providing nourishment to the plants.
Water Pump
- Circulates the water throughout the system, ensuring that both the fish and plants have access to clean, oxygenated water.
- The pump helps maintain the water’s temperature and pH levels, creating a stable environment for the ecosystem.
Filtration System
- Removes solid waste and other impurities from the water, keeping it clean and healthy for the fish and plants.
- Biological filtration, using beneficial bacteria, helps convert toxic ammonia into less harmful nitrates, which can be utilized by plants as nutrients.
Step-by-Step Setup Guide
Setting up an aquaponics system involves a well-planned process. Follow this comprehensive guide to ensure a successful and efficient system:
Tank Selection and Fish Stocking
Choose a fish tank that suits your space and fish requirements. Determine the fish species and their stocking density, ensuring they have ample swimming space. Cycle the tank before adding fish to establish beneficial bacteria.
Plant Selection and Planting
Select plants compatible with your fish and water conditions. Consider plant size, nutrient requirements, and growth habits. Plant densely to maximize nutrient uptake and provide hiding places for fish.
Water Circulation and Filtration
Establish a water circulation system to oxygenate the water and transport nutrients to plants. Install a pump to circulate water from the fish tank to the grow beds and back. Incorporate a filter to remove solid waste and maintain water quality.
Plant and Fish Species Selection

Selecting the right plant and fish species is crucial for the success of an aquaponics system. Considerations should be given to the nutrient requirements of the plants, as well as the tolerance of the fish to the water quality parameters.
Plant species should be chosen based on their nutrient requirements and their ability to thrive in the water conditions created by the fish waste. Some plants, such as leafy greens and herbs, have low nutrient requirements and can tolerate a wide range of water quality parameters.
Other plants, such as fruiting vegetables and flowers, have higher nutrient requirements and may require additional supplementation.
Fish Species Selection
Fish species should be selected based on their tolerance to the water quality parameters created by the plants. Some fish species, such as tilapia and catfish, are tolerant of a wide range of water quality parameters and can thrive in aquaponics systems.
Other fish species, such as salmon and trout, have more specific water quality requirements and may not be suitable for aquaponics systems.
Examples of Suitable Species
Here are some examples of suitable plant and fish species for beginners in aquaponics:
- Plants:leafy greens (lettuce, spinach, kale), herbs (basil, mint, cilantro), fruiting vegetables (tomatoes, peppers, cucumbers)
- Fish:tilapia, catfish, goldfish, koi
Water Management

Water quality is paramount in aquaponics, as it affects both plant and fish health. Several key parameters need to be monitored and adjusted to maintain a healthy ecosystem.
pH Levels
- Optimal pH range for aquaponics is between 6.5 and 7.5.
- pH levels outside this range can stress fish and inhibit nutrient uptake by plants.
- pH can be adjusted using acid (e.g., nitric acid) or base (e.g., potassium hydroxide).
Dissolved Oxygen
- Dissolved oxygen (DO) levels should be maintained between 5 and 8 mg/L.
- Low DO levels can suffocate fish and impair plant growth.
- DO can be increased by aeration (e.g., air pumps, water fountains).
Ammonia and Nitrate Levels
- Ammonia and nitrate are nitrogen compounds that are produced as waste by fish.
- High levels of ammonia and nitrate can be toxic to fish and plants.
- Ammonia is converted to nitrate by beneficial bacteria in the system.
- Nitrate levels can be controlled by adjusting the fish stocking density and by adding plants that absorb nitrate.
Monitoring and Adjustment
Regular monitoring of water quality parameters is essential to ensure optimal conditions for the aquaponics system. This can be done using test kits or electronic sensors.
Based on the monitoring results, adjustments can be made to the system to maintain the desired water quality. These adjustments may include:
- Adding or removing fish to adjust the stocking density.
- Adjusting the pH using acid or base.
- Increasing aeration to raise DO levels.
- Adding plants to absorb excess nitrate.
Nutrient Management
Aquaponics harnesses the natural synergy between plants and fish, utilizing fish waste as a nutrient source for plants. This symbiotic relationship mimics natural ecosystems, where fish provide nutrients for aquatic plants, and plants filter and purify water for the fish.The
Step by step aquaponics can be a great way to learn about this sustainable farming technique. If you’re looking for a great way to get started, consider getting a mini aquaponics kit . These kits come with everything you need to get started, including a tank, pump, filter, and plants.
Once you have your kit, you can follow the step by step instructions to set up your system and start growing your own food.
nitrogen cycle is central to nutrient management in aquaponics. Fish waste, rich in ammonia, is converted by nitrifying bacteria into nitrites and nitrates. Nitrates are readily absorbed by plants as a primary nutrient for growth and development. This process not only provides essential nutrients for plants but also maintains water quality by removing toxic ammonia from the system.While
fish waste provides a significant source of nutrients, additional supplementation may be necessary to ensure optimal plant growth. This can include adding trace elements like iron, calcium, and potassium, which may not be present in sufficient quantities in fish waste alone.
Monitoring water quality and observing plant growth will help determine the need for additional nutrient supplementation.
Pest and Disease Control
Maintaining a healthy aquaponics system requires proactive pest and disease management. Identifying and addressing these issues promptly is crucial to ensure the well-being of your plants and fish.
Common Pests in Aquaponics
Common pests in aquaponics systems include:
- Aphids
- Whiteflies
- Thrips
- Spider mites
- Snails
- Slugs
Common Diseases in Aquaponics
Common diseases in aquaponics systems include:
- Bacterial infections
- Fungal infections
- Parasitic infections
- Viral infections
Organic and Sustainable Pest and Disease Management, Step by step aquaponics
Organic and sustainable pest and disease management practices focus on preventing and controlling issues naturally, without relying on harsh chemicals.
Methods for Pest Control
- Companion planting
- Beneficial insects
- Physical barriers
- Organic pesticides (e.g., neem oil)
Methods for Disease Control
- Water quality monitoring
- Quarantine of new plants and fish
- Disease-resistant varieties
- Organic treatments (e.g., probiotics, garlic extract)
Troubleshooting and Maintenance: Step By Step Aquaponics

Aquaponics systems require regular maintenance and troubleshooting to ensure the health of both the plants and fish. Common problems and solutions include:
Water Quality Issues
- High ammonia levels:Caused by overfeeding, overcrowding, or insufficient filtration. Solution: Reduce feeding, increase water flow, and clean or replace filters.
- High nitrite levels:Caused by insufficient beneficial bacteria in the biofilter. Solution: Add more biofilter media or seed the system with nitrifying bacteria.
- High nitrate levels:Caused by excessive plant growth or insufficient water changes. Solution: Increase water changes or harvest more plants.
- pH imbalances:Caused by fluctuations in water temperature, CO2 levels, or the addition of chemicals. Solution: Monitor pH levels and adjust as needed using pH buffers or aeration.
Plant Growth Problems
- Stunted growth:Caused by nutrient deficiencies, water quality issues, or insufficient light. Solution: Test water parameters, adjust nutrient levels, and provide adequate lighting.
- Yellowing leaves:Caused by nitrogen deficiency, iron deficiency, or waterlogged roots. Solution: Add nitrogen or iron supplements, and ensure proper drainage.
- Browning leaves:Caused by sunburn, nutrient burn, or pests. Solution: Provide shade, adjust nutrient levels, and control pests.
Fish Health Issues
- Fin rot:Caused by bacterial or fungal infections. Solution: Treat with antibiotics or antifungal medications.
- Gill disease:Caused by water quality issues, parasites, or stress. Solution: Improve water quality, treat with antiparasitic medications, and reduce stress factors.
- Swim bladder disease:Caused by gas buildup in the swim bladder. Solution: Adjust water temperature, feed a high-fiber diet, and treat with antibiotics if necessary.
Maintenance Tips
Regular maintenance is crucial for the long-term health of an aquaponics system. Tips include:
- Monitor water quality regularly and adjust parameters as needed.
- Clean filters regularly to remove debris and maintain beneficial bacteria.
- Harvest plants regularly to prevent nutrient buildup and maintain plant health.
- Inspect fish regularly for signs of disease and treat as necessary.
- Keep the system clean and free of debris to prevent water quality issues.
Conclusion
As you embark on your aquaponics adventure, remember that patience, observation, and a commitment to sustainability are key. By following the principles Artikeld in this guide, you will not only reap the rewards of fresh, nutrient-rich produce but also contribute to a more sustainable and resilient food system.
Embrace the challenge of aquaponics, and let this guide be your trusted companion as you navigate the path towards sustainable food production.
Quick FAQs
What are the key components of an aquaponics system?
The essential components include a fish tank, grow beds, water pump, and filtration system, each playing a crucial role in maintaining a healthy and balanced ecosystem.
How do I choose the right fish and plant species for my aquaponics system?
Consider factors such as plant nutrient requirements and fish tolerance to water quality parameters. Examples of suitable species for beginners include tilapia, catfish, lettuce, and basil.
What is the importance of water quality management in aquaponics?
Water quality is paramount, as it affects the health of both plants and fish. Monitor and adjust pH levels, dissolved oxygen, and ammonia and nitrate levels to ensure optimal conditions.
