Welcome to the fascinating world of aquaponics basics! This comprehensive guide will delve into the fundamentals of this innovative food production system that combines aquaculture (fish farming) and hydroponics (plant cultivation in water). Embark on a journey to discover the symbiotic relationship between fish and plants, unlocking the secrets of sustainable food production.
Aquaponics offers a unique solution to the challenges of traditional agriculture, conserving water, optimizing space, and promoting nutrient-rich plant growth. Join us as we explore the essential components of an aquaponics system, unravel the complexities of water and nutrient management, and delve into the selection of suitable fish species and plants.
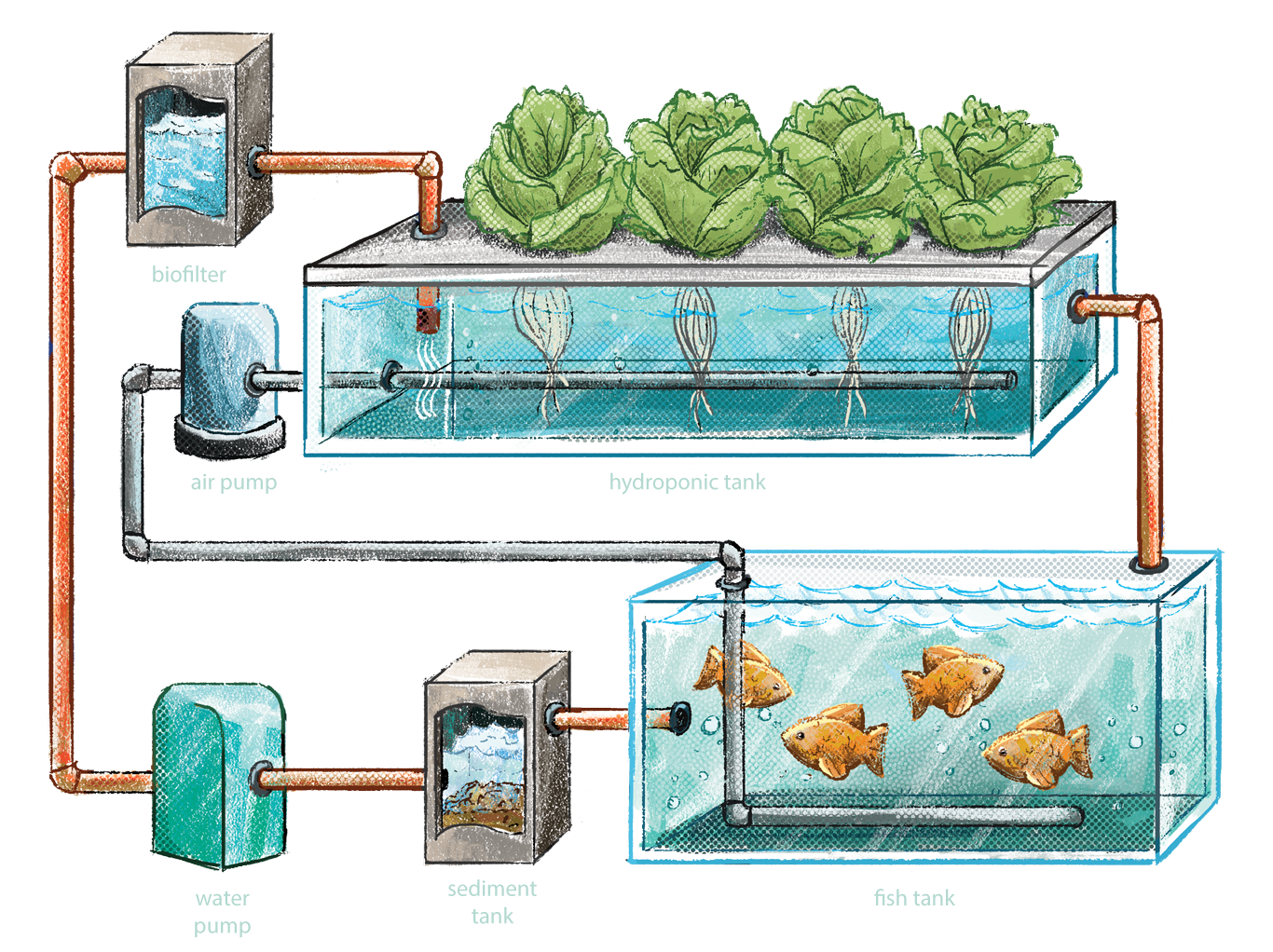
Aquaponics System Overview
Aquaponics is a sustainable and innovative food production system that combines aquaculture (fish farming) and hydroponics (growing plants in water). It creates a closed-loop ecosystem where fish and plants benefit from each other, providing a natural and efficient way to produce food.
In an aquaponics system, fish are raised in tanks or ponds, and their wastewater is used to fertilize plants grown in hydroponic beds. The plants, in turn, filter the water, removing waste products and purifying it for the fish. This symbiotic relationship creates a balanced and sustainable ecosystem that minimizes waste and maximizes resource utilization.
Components of an Aquaponics System
An aquaponics system consists of several essential components that work together to create a symbiotic relationship between fish and plants. These components include:
- Fish tank: The fish tank is where the fish are kept. It provides a controlled environment for the fish to live and grow, and it also serves as a source of nutrients for the plants.
- Grow beds: The grow beds are where the plants are grown. They are typically filled with a growing medium such as gravel or expanded clay pellets, and they are designed to allow the water from the fish tank to flow through them.
- Water filtration system: The water filtration system is responsible for removing waste products from the water. This is important because waste products can build up in the water and harm the fish and plants.
- Aeration system: The aeration system is responsible for providing oxygen to the water. This is important because fish and plants need oxygen to survive.
Plant Selection for Aquaponics: Aquaponics Basics
Selecting suitable plants for your aquaponics system is crucial for its success. Consider the following guidelines to ensure optimal growth and compatibility:
Nutrient Requirements:Plants have varying nutrient requirements. Choose species that thrive in the nutrient-rich water of an aquaponics system. Leafy greens, such as lettuce and spinach, are excellent choices.
Growth Habits:Consider the size and growth pattern of plants. Some species, like tomatoes, require trellising or support, while others, like herbs, can be grown in smaller spaces.
Compatibility with Fish Species:Certain plants may be toxic or incompatible with specific fish species. For example, copper-sensitive fish, such as catfish, should not be paired with plants that accumulate copper, like spinach.
Fish Species for Aquaponics
Selecting suitable fish species is crucial for a successful aquaponics system. Factors to consider include hardiness, tolerance to water conditions, feeding habits, and waste production.
Fish species that are well-suited for aquaponics include:
Tilapia
- Hardy and tolerant to a wide range of water conditions.
- Omnivorous, accepting a variety of plant and animal-based feeds.
- Produce high-quality waste that is beneficial for plants.
Catfish
- Bottom-feeders that help clean the system.
- Tolerant to low oxygen levels and can survive in muddy conditions.
- Omnivorous, but prefer animal-based feeds.
Barramundi
- A high-value fish that is popular in aquaculture.
- Carnivorous, requiring a diet of live or frozen fish.
- Can tolerate a wide range of water conditions.
Water Management in Aquaponics
Maintaining optimal water quality is crucial in aquaponics, as it directly affects the health and growth of both plants and fish. Proper water management involves monitoring and adjusting various parameters, as well as implementing filtration and aeration techniques.
Monitoring Water Quality Parameters
Regular monitoring of water quality parameters is essential to ensure the well-being of the system’s inhabitants. Key parameters to monitor include:
- pH:Optimal pH range for most aquaponics systems is between 6.5 and 7.5. Deviations from this range can affect nutrient uptake by plants and fish metabolism.
- Ammonia:Ammonia is a toxic byproduct of fish waste. Elevated ammonia levels can stress or even kill fish. Regular monitoring is necessary to maintain safe levels.
- Nitrite:Nitrite is an intermediate product of the nitrification process. While less toxic than ammonia, nitrite can still harm fish at high concentrations.
- Nitrate:Nitrate is the final product of the nitrification process and is essential for plant growth. However, excessive nitrate levels can be detrimental to fish health.
Water Filtration and Aeration
In addition to monitoring water quality, implementing water filtration and aeration techniques is crucial for maintaining a healthy aquaponics system. These techniques include:
- Mechanical Filtration:Mechanical filters remove solid particles from the water, reducing the load on biological filters and improving water clarity.
- Biological Filtration:Biological filters contain beneficial bacteria that convert toxic ammonia and nitrite into less harmful nitrate. They are essential for maintaining a healthy environment for fish.
- Aeration:Aeration provides oxygen to the water, which is vital for both fish and beneficial bacteria. It also helps remove excess carbon dioxide and prevent water stagnation.
Nutrient Management in Aquaponics
Nutrient management is crucial in aquaponics, ensuring optimal plant growth and fish health. The key nutrient source in aquaponics is fish waste, which contains essential nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium. These nutrients are released into the water through fish respiration, excretion, and uneaten feed.
Balancing Nutrient Levels
To support plant growth, it’s essential to balance nutrient levels in the aquaponics system. The ideal nutrient ratios for plants vary depending on the species, but generally, a balanced system should have a nitrate-to-phosphate ratio of 10:1. Nitrate is the primary nitrogen source for plants, while phosphate is essential for root development and energy transfer.
Aquaponics basics involve the integration of aquaculture and hydroponics. In hydroponics, hydrogen peroxide is sometimes used as a disinfectant and oxidizer to control pathogens and enhance root development. By integrating hydroponics hydrogen peroxide into aquaponics systems, you can improve water quality, reduce disease risks, and boost plant growth, ultimately enhancing the overall efficiency and sustainability of your aquaponics setup.
Monitoring nutrient levels through regular water testing is crucial to ensure they remain within optimal ranges.
Nutrient Supplementation
In some cases, nutrient supplementation may be necessary to meet plant requirements. This can involve adding specific fertilizers or using additives like iron chelates or potassium supplements. It’s important to carefully monitor nutrient levels to avoid over-fertilization, which can lead to nutrient toxicity and algae blooms.
Managing Organic Matter
Organic matter from fish waste and plant debris can accumulate in the aquaponics system, potentially leading to nutrient imbalances and water quality issues. To manage organic matter, it’s important to:
- Regularly remove solid waste from the fish tank.
- Use a biofilter to break down organic matter and convert it into plant-available nutrients.
- Incorporate plants that absorb excess nutrients, such as duckweed or water hyacinth.
By implementing these nutrient management strategies, aquaponics systems can provide a sustainable and nutrient-rich environment for both plants and fish, maximizing productivity and overall system health.
Benefits of Aquaponics
Aquaponics, an integrated food production system that combines aquaculture (fish farming) and hydroponics (plant cultivation), offers numerous advantages. These benefits make aquaponics a sustainable and efficient approach to food production.
Aquaponics provides several key benefits, including:
Sustainable Food Production
Aquaponics enables sustainable food production by utilizing a closed-loop system. Fish waste provides nutrients for plants, while plants help purify water for fish. This symbiotic relationship reduces the need for external inputs, such as chemical fertilizers and pesticides, resulting in a more environmentally friendly food production method.
Water Conservation
Aquaponics is highly water-efficient. The recirculating water system conserves water by eliminating the need for traditional irrigation methods. The water used in the system is constantly filtered and reused, minimizing water loss and reducing the environmental impact associated with water-intensive agriculture.
Space Efficiency, Aquaponics basics
Aquaponics systems are space-efficient, allowing for food production in urban areas or areas with limited land availability. The vertical integration of fish tanks and plant beds maximizes space utilization, enabling high-yield production in a compact footprint.
Challenges in Aquaponics

Aquaponics, while a promising and sustainable food production system, is not without its challenges. Overcoming these hurdles is essential for successful implementation and long-term viability.
Disease Management
Disease management is a crucial aspect of aquaponics. The close integration of fish and plants creates a unique environment that can facilitate the spread of pathogens. Maintaining optimal water quality, implementing quarantine protocols, and employing preventative measures are essential to mitigate disease outbreaks.
System Maintenance
Aquaponics systems require regular maintenance to ensure their proper functioning. This includes cleaning and inspecting tanks, filters, and pumps, as well as monitoring water parameters and adjusting them as needed. Regular maintenance helps prevent system failures and ensures the health and productivity of both fish and plants.
Cost Considerations
Establishing an aquaponics system can be a significant investment. Factors such as system size, equipment costs, and energy consumption must be carefully considered. Careful planning and budgeting are essential to ensure the economic viability of the system over the long term.
Last Recap

As you delve into the intricacies of aquaponics basics, you’ll gain a profound understanding of this sustainable food production system. From the harmonious coexistence of fish and plants to the delicate balance of water and nutrient management, aquaponics empowers individuals to cultivate their own fresh, healthy produce while minimizing environmental impact.
Embrace the challenge, experiment with different techniques, and unlock the full potential of aquaponics.
Common Queries
What is the fundamental concept behind aquaponics?
Aquaponics is a closed-loop ecosystem where fish and plants coexist in a symbiotic relationship. Fish waste provides nutrients for plants, while plants filter and purify the water for the fish.
What are the essential components of an aquaponics system?
A typical aquaponics system includes a fish tank, grow beds, water filtration system, and aeration system.
How do I select suitable plants for aquaponics?
Consider factors such as nutrient requirements, growth habits, and compatibility with the fish species.
What fish species are commonly used in aquaponics?
Tilapia, catfish, and bass are popular choices due to their hardiness, tolerance to water conditions, and waste production.
Why is water quality management crucial in aquaponics?
Maintaining optimal pH, ammonia, nitrite, and nitrate levels ensures the health and well-being of both fish and plants.
