What is aquaponics system – Welcome to the fascinating world of aquaponics systems, where the harmonious coexistence of fish and plants creates a sustainable and innovative approach to food production. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the captivating details of aquaponics, unraveling its principles, components, and countless benefits.
Embark on a journey to understand how these systems harness the symbiotic relationship between aquatic life and plant growth, offering a glimpse into the future of sustainable agriculture.
Definition and Overview of Aquaponics System
Aquaponics is an innovative food production system that combines aquaculture (fish farming) with hydroponics (plant cultivation in water). This symbiotic integration creates a closed-loop ecosystem where fish waste provides nutrients for plants, while plants filter and purify water for fish.
Principles of Aquaponics
The core principle of aquaponics is the symbiotic relationship between fish and plants. Fish produce waste in the form of ammonia, which is toxic to them. However, beneficial bacteria convert ammonia into nitrates, which are essential nutrients for plants. Plants absorb these nitrates, removing them from the water and purifying it for the fish.
Components of an Aquaponics System: What Is Aquaponics System
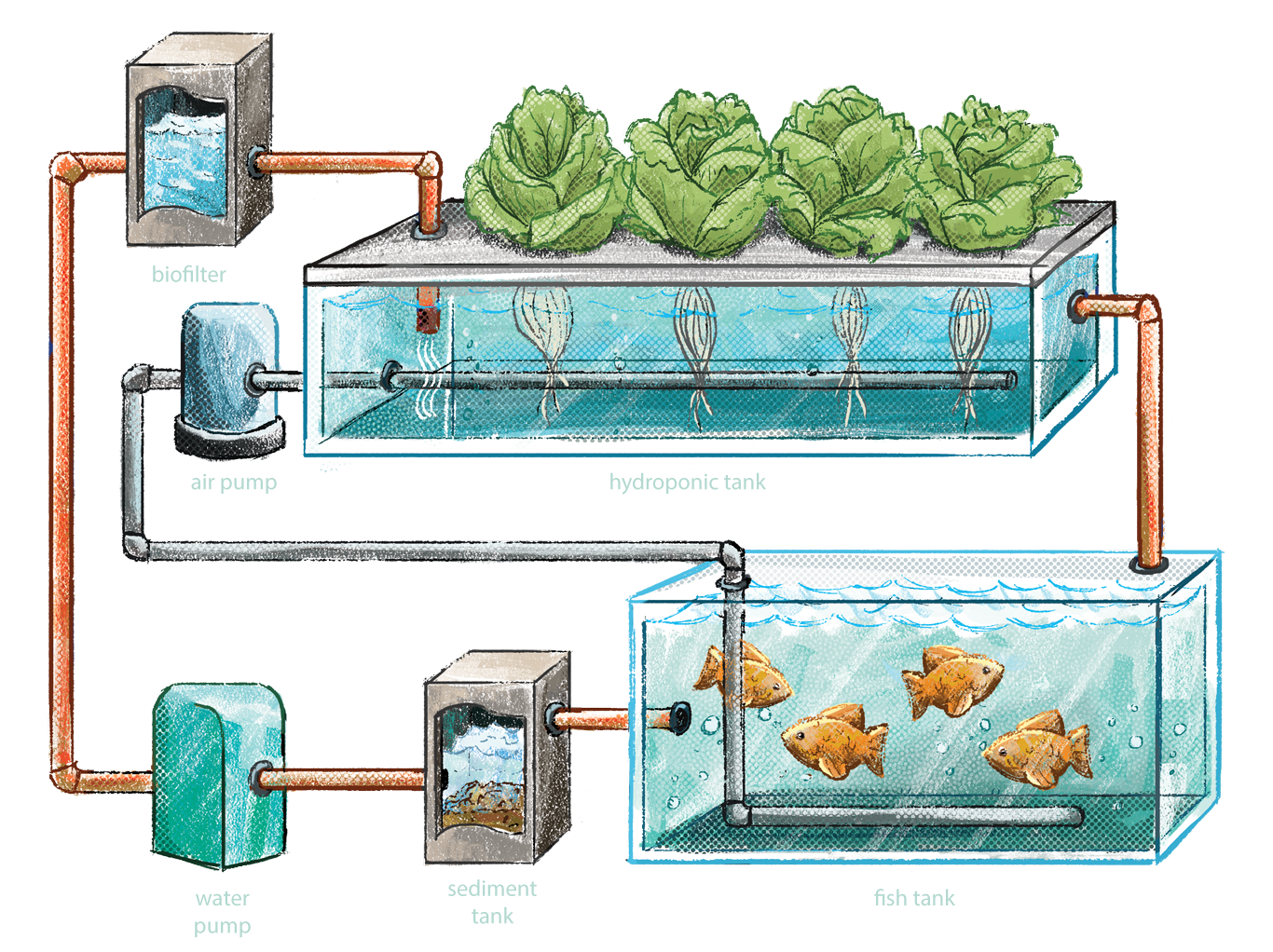
An aquaponics system is a sustainable food production method that combines aquaculture (fish farming) with hydroponics (plant cultivation). It consists of several essential components that work together to create a balanced and efficient ecosystem.
Fish Tank or Aquaculture Unit
The fish tank is the heart of the aquaponics system, where fish are raised and provide the nutrient-rich water for the plants.
- The size and type of fish tank will depend on the number and species of fish being raised.
- It should be equipped with a filtration system to remove waste and maintain water quality.
- The fish tank should also provide adequate oxygen and shelter for the fish.
Grow Beds or Plant Cultivation Area
The grow beds are where the plants are grown in the aquaponics system.
- Grow beds can be made from a variety of materials, such as gravel, sand, or expanded clay pellets.
- They should be designed to provide good drainage and aeration for the plant roots.
- The grow beds should also be sized appropriately for the number and size of plants being grown.
Water Filtration and Recirculation System
The water filtration and recirculation system is responsible for removing waste from the fish tank and delivering nutrient-rich water to the grow beds.
- The filtration system can include mechanical filters, biological filters, and chemical filters.
- The recirculation system uses a pump to move the water from the fish tank to the grow beds and back again.
- The filtration and recirculation system should be designed to maintain water quality and prevent disease in the fish and plants.
Design and Setup of an Aquaponics System

Designing and setting up an aquaponics system requires careful planning and consideration of various factors. This involves determining the system size, selecting suitable fish and plant species, and implementing effective water quality management strategies.
System Size and Capacity
The size and capacity of the aquaponics system will depend on factors such as the intended production goals, available space, and budget. It is crucial to determine the desired output, whether it be for personal consumption, commercial purposes, or educational initiatives.
The system size should be large enough to accommodate the number of fish and plants required to meet production targets. Consider the growth rates, space requirements, and feed conversion ratios of the chosen species.
Fish and Plant Species Selection
The choice of fish and plant species is essential for a successful aquaponics system. Fish species should be compatible with the water quality requirements of the selected plants and have a good feed conversion ratio. Common choices include tilapia, catfish, and trout.
Plant species should be selected based on their nutrient requirements, growth habits, and tolerance to the water conditions. Some popular choices include leafy greens (e.g., lettuce, spinach), herbs (e.g., basil, mint), and fruiting vegetables (e.g., tomatoes, cucumbers).
Water Quality Management
Maintaining optimal water quality is critical for the health of both fish and plants in an aquaponics system. Regular monitoring of water parameters such as pH, dissolved oxygen, ammonia, and nitrates is essential.
Implementing effective filtration and aeration systems is crucial to remove waste products and provide sufficient oxygen for the fish. Biofilters, which utilize beneficial bacteria to convert ammonia into less toxic nitrates, are commonly used in aquaponics systems.
Benefits and Applications of Aquaponics Systems

Aquaponics systems offer a range of benefits, including sustainable food production, water conservation, and nutrient recycling.
Aquaponics systems can be used in various settings, including commercial food production, urban agriculture, and educational and research settings.
Benefits of Aquaponics Systems, What is aquaponics system
Sustainable Food Production
Aquaponics systems can produce food year-round, regardless of climate or weather conditions. They are also more efficient than traditional agriculture, using less water and land.
Water Conservation
Aquaponics systems recycle water, which means that very little water is lost to evaporation or runoff. This makes them an ideal solution for areas with limited water resources.
Nutrient Recycling
Aquaponics systems recycle nutrients from fish waste, which means that no additional fertilizers are needed. This makes them a more environmentally friendly option than traditional agriculture.
Applications of Aquaponics Systems
Commercial Food Production
Aquaponics systems are being used to produce food commercially in many parts of the world. They are particularly well-suited for producing high-value crops, such as leafy greens, herbs, and fish.
Urban Agriculture
Aquaponics systems are also being used in urban areas to produce food locally. They are a great way to grow fresh, healthy food in a small space.
An aquaponics system is a sustainable method that combines aquaculture, the raising of aquatic animals, and hydroponics, the growing of plants in water. It’s a closed-loop system where the nutrient-rich water from the fish tanks is used to fertilize the plants, and the plants, in turn, help clean the water for the fish.
To learn more about the differences between aquaponics and aquaculture, click here . Aquaponics is a great way to grow food and raise fish in a sustainable and environmentally friendly way.
Educational and Research Settings
Aquaponics systems are also being used in educational and research settings to teach students about sustainable food production. They are also being used to research new ways to improve aquaponics technology.
Challenges and Considerations in Aquaponics Systems
Operating aquaponics systems presents several challenges that require careful attention and management. These include:
Disease Management
Maintaining a healthy environment for both fish and plants is crucial in aquaponics. Diseases can arise from various sources, including bacteria, fungi, and parasites. Regular monitoring of water quality, timely detection of symptoms, and appropriate treatment measures are essential for disease prevention and control.
Water Quality Fluctuations
Aquaponics systems require stable water quality to ensure the well-being of both fish and plants. Fluctuations in pH, dissolved oxygen levels, ammonia, and nitrite concentrations can negatively impact the system. Monitoring and adjusting water parameters regularly, implementing water filtration and aeration systems, and maintaining optimal stocking densities are key to maintaining water quality.
Energy Consumption
Aquaponics systems often require energy for water pumps, aeration systems, and lighting. The energy consumption can be significant, especially in large-scale operations. Exploring energy-efficient technologies, optimizing system design, and utilizing renewable energy sources can help minimize energy consumption.
Final Review
As we conclude our exploration of aquaponics systems, it’s evident that they hold immense promise for addressing global food security and environmental challenges. Their ability to conserve water, recycle nutrients, and provide a reliable source of fresh produce makes them a beacon of hope in a world facing increasing resource constraints.
Whether implemented on a commercial scale or in urban settings, aquaponics systems have the potential to transform our food production practices and inspire future generations to embrace sustainable living.
User Queries
What are the key components of an aquaponics system?
An aquaponics system typically comprises a fish tank, grow beds, a water filtration system, and a recirculation pump.
How does an aquaponics system work?
Fish waste provides nutrients for plants, which in turn purify the water for the fish. This symbiotic relationship creates a closed-loop system that minimizes waste and optimizes resource utilization.
What are the benefits of aquaponics systems?
Aquaponics offers numerous advantages, including sustainable food production, water conservation, nutrient recycling, and the potential for year-round cultivation in controlled environments.
