Severe vertigo attacks, characterized by intense dizziness and a false sense of movement, can be debilitating and disrupt daily life. This comprehensive guide delves into the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and management of severe vertigo attacks, empowering you with the knowledge to effectively address this condition.
Definition and Symptoms
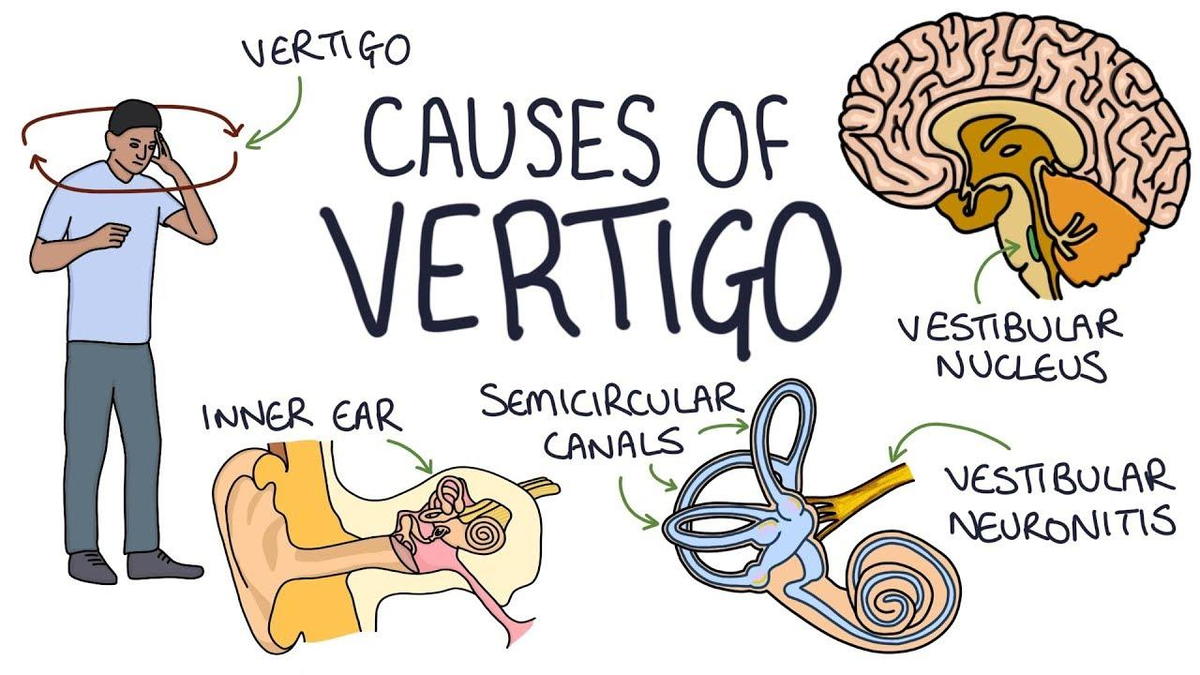
A severe vertigo attack is a sudden, intense episode of dizziness that can cause nausea, vomiting, and balance problems. It is often caused by a problem with the inner ear, which is responsible for balance and hearing.
Symptoms of a severe vertigo attack can include:
- Spinning sensation
- Nausea and vomiting
- Balance problems
- Difficulty walking or standing
- Headaches
- Tinnitus (ringing in the ears)
- Hearing loss
Vertigo attacks can last for minutes, hours, or even days. They can occur occasionally or frequently, depending on the underlying cause.
Causes and Risk Factors

Severe vertigo attacks can stem from various underlying medical conditions. Understanding these causes and identifying potential risk factors can help in managing and preventing future episodes.
Underlying medical conditions that may trigger severe vertigo include:
- Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV): A common cause, involving loose crystals in the inner ear that move and trigger vertigo when the head is moved.
- Ménière’s disease: A condition characterized by fluid buildup in the inner ear, causing vertigo, hearing loss, and tinnitus.
- Vestibular neuritis: Inflammation of the vestibular nerve, which transmits balance signals from the inner ear to the brain.
- Acoustic neuroma: A non-cancerous tumor on the vestibular nerve, which can cause hearing loss and vertigo.
- Migraine: Severe headaches that can be accompanied by vertigo.
- Multiple sclerosis: A neurological disorder that can affect the brain and spinal cord, potentially causing vertigo.
Risk Factors
Certain factors can increase the risk of experiencing severe vertigo attacks:
- Age: Vertigo is more common in people over the age of 50.
- Lifestyle choices: Smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and poor sleep hygiene can contribute to vertigo.
- Medications: Some medications, such as antibiotics, anticonvulsants, and aspirin, can cause vertigo as a side effect.
- Head injuries: Trauma to the head can damage the vestibular system and lead to vertigo.
- Genetic predisposition: Some people may have a genetic predisposition to developing vertigo.
Diagnosis and Treatment

To determine the cause of severe vertigo attacks, doctors will perform a comprehensive evaluation, including a physical exam, a detailed medical history, and diagnostic tests.
Once the underlying cause is identified, the appropriate treatment plan can be developed. Treatment options vary depending on the underlying cause and may include medications, physical therapy, or surgical interventions.
Medications
Medications can be used to relieve symptoms of vertigo and prevent future attacks. Common medications used include anti-nausea drugs, anti-vertigo drugs, and sedatives.
If you’re experiencing a severe vertigo attack, it’s important to seek medical attention immediately. While there are a number of potential causes of vertigo, from benign to serious, your doctor can help you determine the underlying cause and recommend the best course of treatment.
For more information on vertigo cures and causes, visit vertigo cures and causes . Severe vertigo attacks can be debilitating, but with proper diagnosis and treatment, you can get back to living a normal life.
- Anti-nausea drugs help reduce nausea and vomiting associated with vertigo.
- Anti-vertigo drugs work by suppressing the activity of the vestibular system, which is responsible for balance.
- Sedatives can help reduce anxiety and dizziness associated with vertigo.
Physical Therapy
Physical therapy can help improve balance and reduce the frequency and severity of vertigo attacks. Exercises may include:
- Vestibular rehabilitation exercises: These exercises are designed to retrain the brain to compensate for vestibular dysfunction.
- Balance exercises: These exercises help improve balance and stability.
- Neck exercises: These exercises help improve neck mobility and reduce symptoms of cervical vertigo.
Surgical Interventions, Severe vertigo attack
In some cases, surgery may be necessary to treat severe vertigo attacks. Surgical options include:
- Vestibular nerve section: This surgery involves cutting the vestibular nerve, which sends signals from the inner ear to the brain.
- Labyrinthine surgery: This surgery involves removing or repairing the labyrinth, which is the part of the inner ear responsible for balance.
The effectiveness of each treatment method varies depending on the underlying cause of vertigo. It is important to discuss the potential benefits and risks of each treatment option with your doctor to determine the best course of action.
Management and Prevention: Severe Vertigo Attack
Effectively managing severe vertigo attacks during episodes and implementing lifestyle modifications can significantly reduce their frequency and severity. Additionally, regular medical follow-ups are crucial for monitoring progress and adjusting treatment plans as needed.
Managing Vertigo Attacks
- Rest and avoid sudden movements:Lie down in a quiet, dark room and minimize head movements to reduce dizziness.
- Focus on a stationary object:Fix your gaze on a stable point to help stabilize your balance and reduce nausea.
- Hydrate:Dehydration can worsen vertigo symptoms, so stay hydrated by drinking plenty of fluids.
- Consider over-the-counter medications:Antihistamines or meclizine can help relieve nausea and dizziness associated with vertigo.
- Try the Epley maneuver:This simple exercise can help reposition ear crystals that may be causing vertigo.
Preventing Vertigo Attacks
While not all causes of vertigo are preventable, certain lifestyle modifications can reduce the risk of future attacks:
- Avoid caffeine and alcohol:These substances can worsen vertigo symptoms.
- Get regular exercise:Maintaining a healthy weight and engaging in regular physical activity can improve balance and circulation.
- Manage stress:Stress can trigger vertigo attacks, so find healthy ways to cope with stress, such as exercise, meditation, or yoga.
- Avoid sudden head movements:Be cautious when turning your head or bending over, especially if you have a history of vertigo.
- Consider a low-sodium diet:Excess sodium can contribute to fluid retention, which can worsen vertigo.
Regular Medical Follow-ups
Regular check-ups with your healthcare provider are essential for monitoring the effectiveness of your treatment plan and making necessary adjustments. They can also provide guidance on lifestyle modifications and other preventive measures.
Related Conditions

Severe vertigo attacks can share symptoms with other conditions. It’s crucial to differentiate between them to ensure appropriate treatment.
Conditions that mimic vertigo include:
- Vestibular neuritis: An inflammation of the vestibular nerve that affects balance.
- Meniere’s disease: A disorder of the inner ear that causes vertigo, hearing loss, and tinnitus.
- Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV): A condition where tiny crystals in the inner ear shift, causing brief episodes of vertigo.
- Migraine-associated vertigo: Vertigo that occurs as a symptom of migraines.
Differential Diagnosis
Differentiating between these conditions requires a thorough medical history and physical examination. Doctors may use tests like:
- Audiometry: To assess hearing function.
- Electronystagmography (ENG): To measure eye movements.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): To visualize the brain and inner ear.
Potential Complications
Untreated severe vertigo attacks can lead to complications, including:
- Falls and injuries
- Motion sickness
- Anxiety and depression
- Reduced quality of life
Long-term effects of severe vertigo attacks can include:
- Persistent dizziness
- Difficulty with balance and coordination
- Reduced mobility and independence
Closing Notes
Understanding severe vertigo attacks is crucial for effective management and prevention. By recognizing the symptoms, seeking prompt medical attention, and adhering to treatment plans, individuals can regain control over their well-being and minimize the impact of this condition on their lives.
