A severe case of vertigo, a debilitating condition characterized by intense dizziness, can significantly impact one’s daily life. This comprehensive guide delves into the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and management strategies for this condition, empowering individuals with the knowledge and tools to navigate their journey towards recovery.
Vertigo, a sensation of spinning or movement when there is none, can be a distressing and disorienting experience. When the symptoms become severe, it can significantly impair mobility, balance, and overall well-being. Understanding the underlying causes and effective management techniques is crucial for regaining control over one’s life and minimizing the impact of vertigo.
Symptoms of a Severe Case of Vertigo

A severe case of vertigo can cause intense dizziness, nausea, vomiting, and difficulty walking. These symptoms can make it difficult to perform everyday activities, such as driving, working, or even just walking around.
Dizziness
Dizziness is the most common symptom of vertigo. It can feel like you are spinning or moving, even when you are standing still. Dizziness can be so severe that it makes it difficult to walk or even stand up.
Nausea and Vomiting
Nausea and vomiting are also common symptoms of vertigo. These symptoms can be caused by the imbalance in the inner ear, which can affect the stomach and digestive system.
Difficulty Walking
Difficulty walking is another common symptom of vertigo. This can be caused by the dizziness and nausea, which can make it difficult to balance and walk. In some cases, vertigo can also cause double vision, which can make it even more difficult to walk.
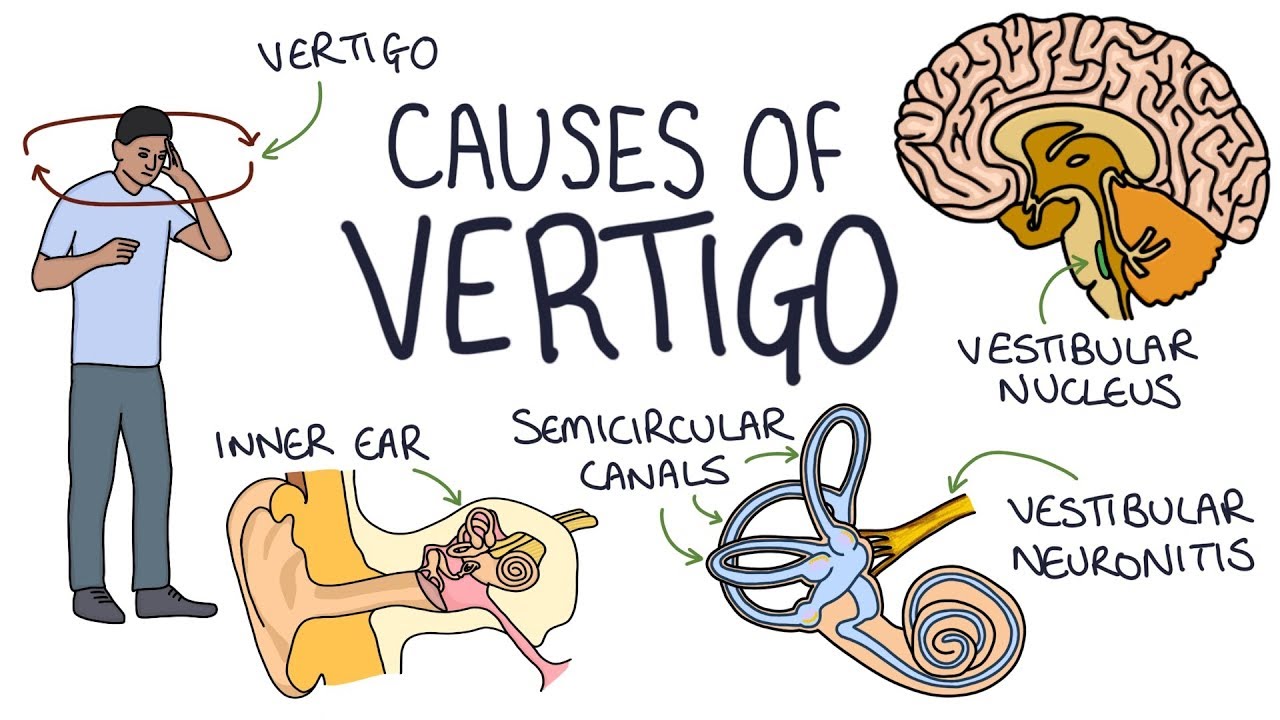
Causes of a Severe Case of Vertigo
Severe vertigo can be caused by a variety of underlying medical conditions. Some of the most common causes include:
- Vestibular neuritis:This is an inflammation of the vestibular nerve, which is responsible for balance. It can cause sudden onset of severe vertigo, along with nausea, vomiting, and hearing loss.
- Meniere’s disease:This is a disorder of the inner ear that can cause episodes of severe vertigo, hearing loss, and tinnitus (ringing in the ears).
- Acoustic neuroma:This is a non-cancerous tumor that grows on the vestibular nerve. It can cause progressive hearing loss, tinnitus, and vertigo.
The prevalence of these conditions varies, but vestibular neuritis is the most common cause of severe vertigo, accounting for about 40% of cases. Meniere’s disease is less common, affecting about 1 in 1,000 people, while acoustic neuroma is rare, affecting about 1 in 100,000 people.
Risk factors for these conditions include age, certain medical conditions (such as diabetes and high blood pressure), and exposure to certain toxins (such as alcohol and tobacco).
Diagnosis of a Severe Case of Vertigo

A thorough medical history and physical examination are crucial in diagnosing a severe case of vertigo. The healthcare professional will inquire about the patient’s symptoms, including the duration, severity, and any associated symptoms. The physical examination will involve tests to assess the patient’s balance, coordination, and eye movements.
Balance Tests
Balance tests evaluate the patient’s ability to maintain balance and detect any abnormalities in the vestibular system. These tests may include:
Romberg test
The patient stands with their feet together and eyes closed. The healthcare professional assesses the patient’s ability to maintain balance for 30 seconds.
Fukuda stepping test
The patient takes 10 steps forward and 10 steps backward with their eyes closed. The healthcare professional observes the patient’s gait and any deviations from a straight line.
Dix-Hallpike maneuver
The patient sits on an examination table with their head turned 45 degrees to one side. The healthcare professional quickly lowers the patient’s head and neck to a supine position. The patient is observed for any nystagmus (involuntary eye movements) or vertigo.
Imaging Studies
Imaging studies may be recommended to further evaluate the underlying cause of vertigo. These studies may include:
Computed tomography (CT) scan
A CT scan provides detailed images of the brain and inner ear, which can help identify structural abnormalities.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
An MRI scan uses magnetic fields and radio waves to produce detailed images of the brain and inner ear. It can detect abnormalities in the vestibular system, such as tumors or inflammation.
Electronystagmography (ENG)
ENG measures eye movements and can help identify abnormalities in the vestibular system.
Role of a Healthcare Professional
An accurate diagnosis of a severe case of vertigo requires a thorough evaluation by a healthcare professional, such as an otolaryngologist (ear, nose, and throat specialist) or neurologist. The healthcare professional will use their expertise to interpret the patient’s symptoms, perform the necessary tests, and make an accurate diagnosis.
A severe case of vertigo can be debilitating, making it difficult to perform everyday activities. If you’re experiencing severe vertigo, it’s important to seek medical attention to rule out any underlying medical conditions. In some cases, over-the-counter vertigo medication can help to relieve symptoms.
However, it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional before taking any medication, as some medications may interact with other medications you’re taking or may not be appropriate for your condition. A severe case of vertigo can be a frightening experience, but with the right treatment, you can get your life back on track.
Based on the diagnosis, the healthcare professional will recommend the appropriate treatment plan.
Treatment Options for a Severe Case of Vertigo
Managing a severe case of vertigo requires a comprehensive approach involving various treatment options. The choice of treatment depends on the underlying cause and the severity of symptoms. Here are the primary treatment approaches:
Treatment options for a severe case of vertigo include medication, physical therapy, and surgical intervention. Each treatment option has its own effectiveness and potential side effects.
Medication
- Anti-vertigo medications:These medications help suppress nausea, vomiting, and dizziness associated with vertigo. Common examples include meclizine, promethazine, and scopolamine.
- Vestibular suppressants:These medications reduce the activity of the vestibular system, which is responsible for balance and spatial orientation. Examples include benzodiazepines (such as diazepam and lorazepam) and anticholinergics (such as scopolamine and trihexyphenidyl).
- Diuretics:In some cases, diuretics may be prescribed to reduce fluid retention in the inner ear, which can contribute to vertigo.
It’s important to note that medications can have side effects such as drowsiness, dry mouth, blurred vision, and difficulty concentrating. The choice and dosage of medication should be carefully determined by a healthcare professional based on the individual’s needs and response to treatment.
Management of a Severe Case of Vertigo
Managing a severe case of vertigo requires a multifaceted approach that encompasses lifestyle modifications, coping mechanisms, support groups, and regular medical follow-ups.
Lifestyle modifications play a crucial role in reducing the frequency and severity of vertigo episodes. These include avoiding sudden head movements, limiting caffeine and alcohol intake, and getting adequate sleep. Additionally, engaging in regular exercise can help improve balance and coordination.
Coping Mechanisms
- Vestibular rehabilitation exercises: These exercises aim to retrain the balance system and reduce dizziness.
- Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT): CBT helps individuals manage the psychological aspects of vertigo, such as anxiety and fear.
- Relaxation techniques: Techniques like deep breathing and meditation can help reduce stress and improve coping abilities.
Support Groups
Joining support groups can provide emotional support and practical advice from individuals who have experienced similar challenges.
Regular Follow-Up Appointments, Severe case of vertigo
Regular follow-up appointments with a healthcare professional are essential for monitoring the condition, adjusting treatment plans, and addressing any complications. These appointments also provide an opportunity for individuals to discuss their progress and concerns.
Final Conclusion

Managing a severe case of vertigo requires a multifaceted approach that encompasses medical interventions, lifestyle modifications, and emotional support. By working closely with healthcare professionals, adopting coping mechanisms, and seeking support from family, friends, or support groups, individuals can effectively manage their symptoms and improve their quality of life.
Remember, you are not alone in this journey, and with the right knowledge and support, you can regain control over your life and live fully despite the challenges posed by vertigo.