Delve into the realm of hydroponics and aeroponics, innovative plant cultivation methods that are revolutionizing agriculture. These systems offer a myriad of advantages, including increased yields, reduced water usage, and improved crop quality. Embark on a journey of discovery as we explore the intricacies of these fascinating techniques.
Hydroponics, the art of growing plants in nutrient-rich water, and aeroponics, where plants thrive suspended in a nutrient-infused mist, present unique approaches to plant growth. Dive deeper into their mechanisms, benefits, and challenges as we unravel the secrets of these groundbreaking methods.
Hydroponics vs. Aeroponics
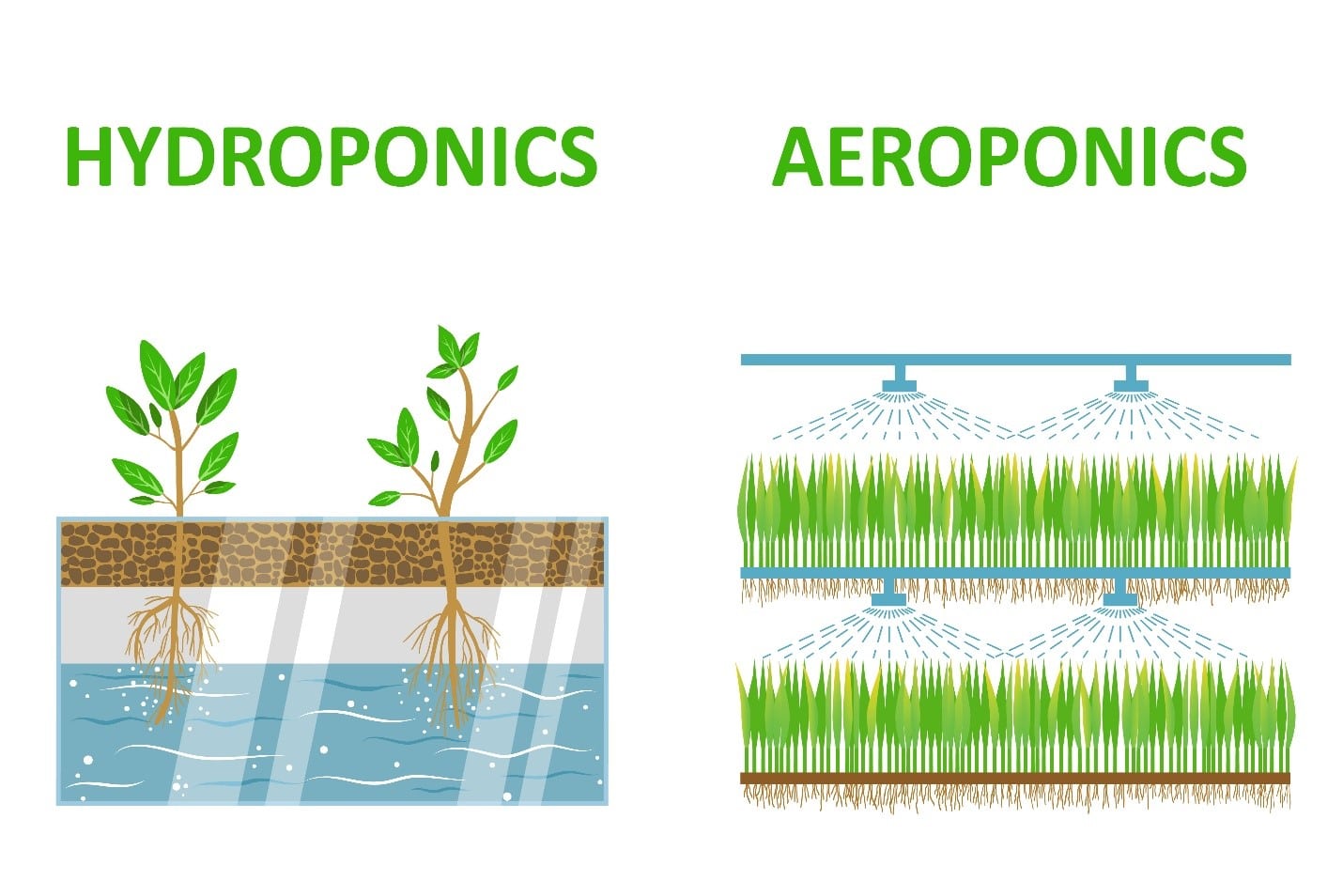
Hydroponics and aeroponics are two popular methods of growing plants without soil. While both methods offer advantages over traditional soil-based gardening, they also have some key differences.
For those passionate about hydroponics and aeroponics, an aquaponics online course can provide valuable insights into the integration of aquaculture and plant cultivation. While hydroponics involves growing plants in nutrient-rich water, aeroponics suspends plant roots in the air and mists them with a nutrient solution.
Understanding these techniques can empower you to optimize your home gardening systems and explore sustainable food production.
The main difference between hydroponics and aeroponics is the way that nutrients are delivered to the plants. In hydroponics, plants are grown in a nutrient-rich water solution. The water is constantly circulated, providing the plants with a continuous supply of nutrients.
In aeroponics, plants are suspended in the air and their roots are misted with a nutrient-rich solution. This method allows the roots to absorb nutrients more efficiently.
Another key difference between hydroponics and aeroponics is the root environment. In hydroponics, the roots of the plants are submerged in water. This can lead to root rot if the water is not properly aerated. In aeroponics, the roots of the plants are exposed to the air.
This allows them to breathe more easily and reduces the risk of root rot.
Finally, hydroponics and aeroponics require different types of equipment. Hydroponics systems typically require a water reservoir, a pump, and a grow bed. Aeroponics systems typically require a misting system, a fan, and a grow chamber.
| Feature | Hydroponics | Aeroponics |
|---|---|---|
| Nutrient delivery | Plants are grown in a nutrient-rich water solution. | Plants are suspended in the air and their roots are misted with a nutrient-rich solution. |
| Root environment | The roots of the plants are submerged in water. | The roots of the plants are exposed to the air. |
| Equipment requirements | Water reservoir, pump, grow bed | Misting system, fan, grow chamber |
Hydroponic Systems
Hydroponic systems provide an alternative growing method that does not rely on soil. Instead, plants are grown in a nutrient-rich water solution, providing them with essential nutrients for growth and development. Various types of hydroponic systems exist, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
Deep Water Culture (DWC)
DWC systems involve suspending plants in a nutrient-rich water solution, providing constant access to oxygen and nutrients. Advantages:
- Efficient use of space
- Simplified monitoring and maintenance
- Reduced risk of root rot
Disadvantages:
- Potential for oxygen deficiency if water levels fluctuate
- Risk of nutrient imbalances or pH fluctuations
- Requires specialized equipment for oxygenation
Nutrient Film Technique (NFT)
NFT systems circulate a thin film of nutrient-rich water over the roots of plants, providing constant nutrient supply and oxygenation. Advantages:
- Rapid plant growth due to continuous nutrient availability
- Efficient use of water and nutrients
- Minimal space requirements
Disadvantages:
- Requires precise control of water flow and nutrient concentration
- Risk of clogging or nutrient imbalances
- Potential for root damage if water flow is interrupted
Ebb and Flow
Ebb and flow systems flood and drain the growing medium with nutrient-rich water at regular intervals. Advantages:
- Provides both aeration and nutrient delivery
- Adaptable to various growing media
- Easy to implement and maintain
Disadvantages:
- Requires a timer or automated system for flooding and draining
- Can be prone to nutrient deficiencies or pH fluctuations if intervals are not optimized
- Potential for root damage if drainage is inadequate
Aeroponic Systems
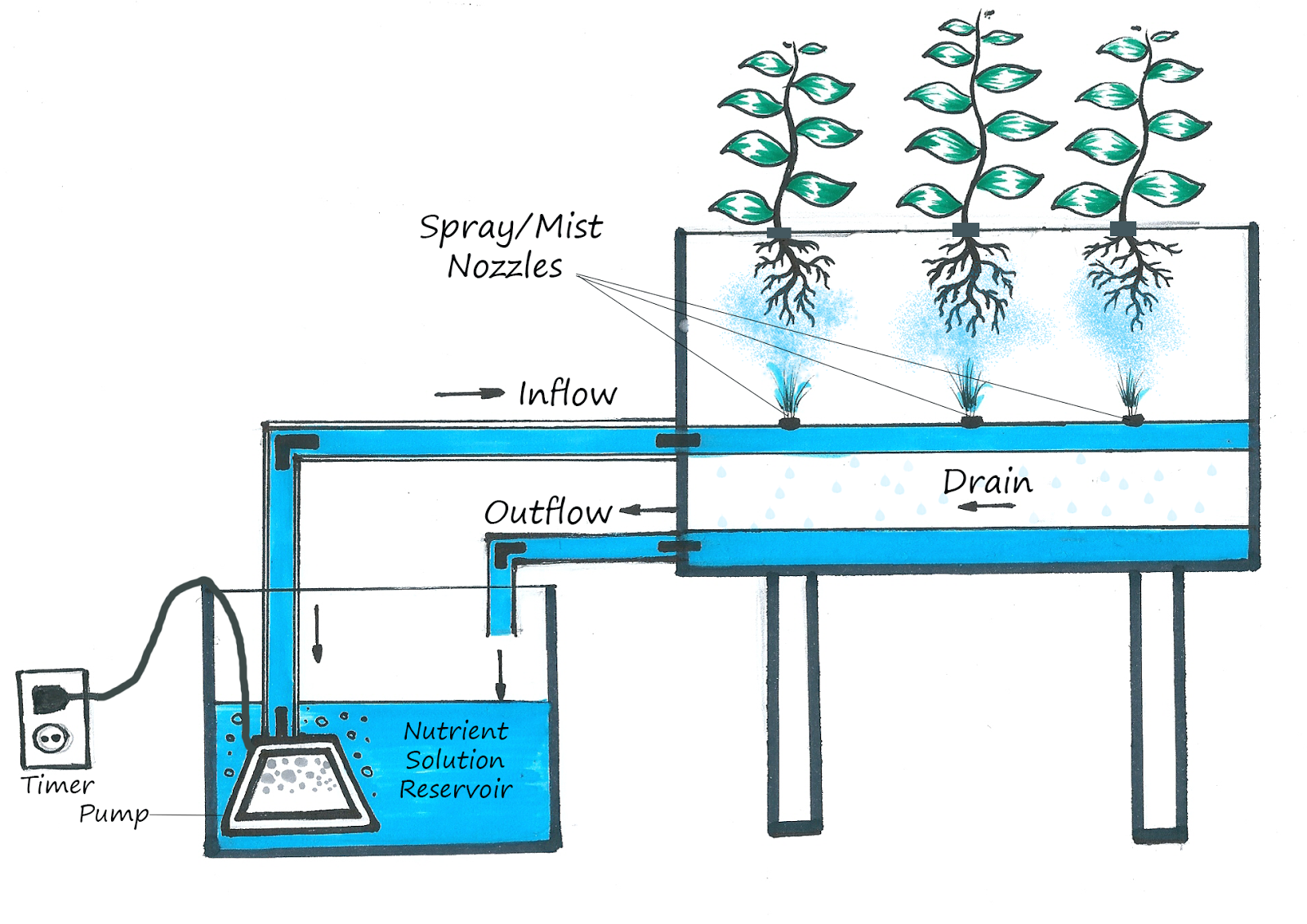
Aeroponics is a type of hydroponics that grows plants in a mist of nutrient-rich water. The roots of the plants are suspended in the air and are constantly misted with water and nutrients. This system provides the plants with a constant supply of oxygen and nutrients, which can lead to faster growth and higher yields.
Nutrient Delivery
In aeroponics, nutrients are delivered to the plants in a mist of water. The mist is created by a pump that circulates the water through a series of nozzles. The nozzles are positioned so that the mist evenly coats the roots of the plants.
Root Development
The constant misting of the roots in aeroponics helps to promote root development. The mist provides the roots with a constant supply of oxygen, which is essential for root growth. The mist also helps to keep the roots clean and free of disease.
Environmental Control
Aeroponics systems offer a high degree of environmental control. The temperature, humidity, and light levels can all be controlled to create an optimal growing environment for the plants. This level of control can help to improve plant growth and yields.
Plant Growth and Yield
Hydroponics and aeroponics offer advantages in plant growth and yield compared to traditional soil-based cultivation. These systems provide optimal conditions for nutrient uptake, water absorption, and root development, leading to faster growth rates and higher yields.
Factors Influencing Plant Growth and Yield, Hydroponics and aeroponics
Several factors influence plant growth and yield in hydroponics and aeroponics, including:
- Nutrient availability:Plants require a balanced supply of essential nutrients for optimal growth. Hydroponic and aeroponic systems allow for precise control of nutrient concentration, ensuring plants receive the necessary nutrients at the right time.
- Light intensity:Light is essential for photosynthesis, the process by which plants convert light energy into chemical energy. Both hydroponics and aeroponics provide optimal light conditions for plant growth, using artificial lighting or natural sunlight.
- Temperature:Temperature plays a crucial role in plant metabolism and growth. Hydroponic and aeroponic systems allow for precise temperature control, maintaining optimal conditions for plant growth and development.
Nutrient Management

Effective nutrient management is crucial for optimal plant growth and yield in both hydroponics and aeroponics. Understanding the nutritional requirements of your plants and monitoring nutrient levels ensures a balanced supply of essential elements.
Regular monitoring of nutrient levels, including pH and electrical conductivity (EC), is essential. Adjust nutrient concentrations as needed to maintain optimal levels. Consider using a nutrient meter or testing kit for accurate measurements.
Monitoring Nutrient Levels
Regularly monitor pH and EC levels in the nutrient solution. pH should be maintained within a specific range, typically between 5.5 and 6.5, to ensure nutrient availability. EC measures the concentration of dissolved salts in the solution and should be adjusted based on plant growth stage and species.
Monitor nutrient levels frequently, especially during rapid growth periods. Use a nutrient meter or testing kit to check for deficiencies or excesses. Adjust nutrient concentrations accordingly to provide a balanced supply of essential elements.
Adjusting Nutrient Levels
Adjust nutrient levels by adding or diluting the nutrient solution. If nutrient levels are too low, add a concentrated nutrient solution. If levels are too high, dilute the solution with water. Gradual adjustments are recommended to avoid shocking the plants.
Follow the nutrient manufacturer’s recommendations as a general guideline. However, adjust nutrient concentrations based on plant growth stage, species, and environmental conditions. Monitor plant health and growth regularly to identify any nutrient deficiencies or excesses.
Environmental Control: Hydroponics And Aeroponics
Environmental control is crucial in both hydroponic and aeroponic systems to ensure optimal plant growth and yield. Various environmental factors need to be closely monitored and regulated to create a suitable growing environment for the plants.
Temperature, humidity, and light intensity are among the most critical factors that directly influence plant growth and development. Let’s delve into each of these factors and their significance:
Temperature
Temperature plays a vital role in plant metabolism and growth rate. Different plant species have varying temperature requirements for optimal growth. Maintaining the appropriate temperature range is essential to prevent stress and ensure proper physiological processes in plants.
In general, most plants prefer a temperature range between 65-75°F (18-24°C). Temperatures outside this range can lead to reduced growth, stunted development, or even plant damage.
Humidity
Humidity refers to the amount of water vapor in the air. It is an important factor in hydroponic and aeroponic systems as it affects plant transpiration and nutrient uptake.
High humidity levels can promote excessive transpiration, leading to water loss and nutrient imbalances in plants. Conversely, low humidity levels can result in dehydration and reduced nutrient absorption. Maintaining optimal humidity levels is crucial to ensure proper plant growth and prevent stress.
Light Intensity
Light intensity is essential for photosynthesis, the process by which plants convert light energy into chemical energy. The amount of light plants receive directly impacts their growth rate, leaf area, and overall yield.
Different plant species have varying light requirements. Some plants, like tomatoes and peppers, thrive in high-light conditions, while others, such as lettuce and herbs, prefer lower light intensities. Providing the appropriate light intensity is crucial for optimizing plant growth and maximizing yield.
Applications and Benefits

Hydroponics and aeroponics offer numerous applications in commercial agriculture, urban farming, and research. In commercial agriculture, these systems enable year-round crop production, regardless of climate or seasonality. They are particularly beneficial for high-value crops such as leafy greens, herbs, and berries.
Benefits of Hydroponics and Aeroponics
These systems provide several benefits, including:
- Increased yield: Controlled environments and optimized nutrient delivery promote rapid plant growth and higher yields compared to traditional soil-based methods.
- Reduced water usage: Hydroponic and aeroponic systems use significantly less water than soil-based cultivation, making them ideal for water-scarce regions.
- Improved crop quality: Precise control over nutrient levels and environmental conditions results in healthier, more nutritious, and aesthetically pleasing crops.
- Year-round production: Indoor hydroponic and aeroponic systems allow for crop cultivation regardless of outdoor weather conditions, enabling year-round production.
- Reduced labor costs: Automated systems and efficient plant spacing minimize labor requirements, leading to lower operating costs.
Challenges and Limitations
Hydroponics and aeroponics, while offering significant advantages, also face certain challenges and limitations.
System Complexity
Hydroponic and aeroponic systems can be complex to design, install, and maintain. They require specialized knowledge of plant nutrition, water management, and environmental control.
Cost
Establishing and operating hydroponic or aeroponic systems can be expensive. The initial investment in equipment, infrastructure, and specialized nutrients can be substantial.
Need for Specialized Knowledge
Successful hydroponic and aeroponic cultivation requires a deep understanding of plant physiology, nutrient management, and environmental control. Growers need to be skilled in monitoring and adjusting system parameters to ensure optimal plant growth.
Final Conclusion
As we conclude our exploration of hydroponics and aeroponics, it becomes evident that these systems hold immense potential for transforming agriculture. Their ability to optimize plant growth, conserve resources, and enhance crop quality makes them invaluable tools for feeding a growing global population.
While challenges remain, ongoing research and innovation promise to further refine these techniques, unlocking even greater possibilities for sustainable and efficient plant cultivation.
Top FAQs
What are the key differences between hydroponics and aeroponics?
In hydroponics, plants are grown in nutrient-rich water, while in aeroponics, they are suspended in a nutrient-infused mist. Aeroponics offers advantages in terms of root oxygenation and nutrient absorption, but requires more precise environmental control.
What are the advantages of hydroponics and aeroponics?
These systems offer increased yields, reduced water usage, improved crop quality, and the ability to grow plants in space-constrained environments.
What are the challenges associated with hydroponics and aeroponics?
Complexity, cost, and the need for specialized knowledge can pose challenges, particularly for large-scale operations.
