Hydroponic system with fish – Discover the remarkable world of hydroponic systems with fish, where plants thrive and fish flourish in a symbiotic dance. Immerse yourself in the benefits, components, and management practices of this innovative and sustainable approach to agriculture.
Harnessing the power of nature, hydroponic systems with fish offer a myriad of advantages, including increased plant growth rates, reduced water usage, and a harmonious ecosystem. Embark on a journey of knowledge and practical insights as we delve into the fascinating world of this integrated farming system.
Introduction to Hydroponic Systems with Fish
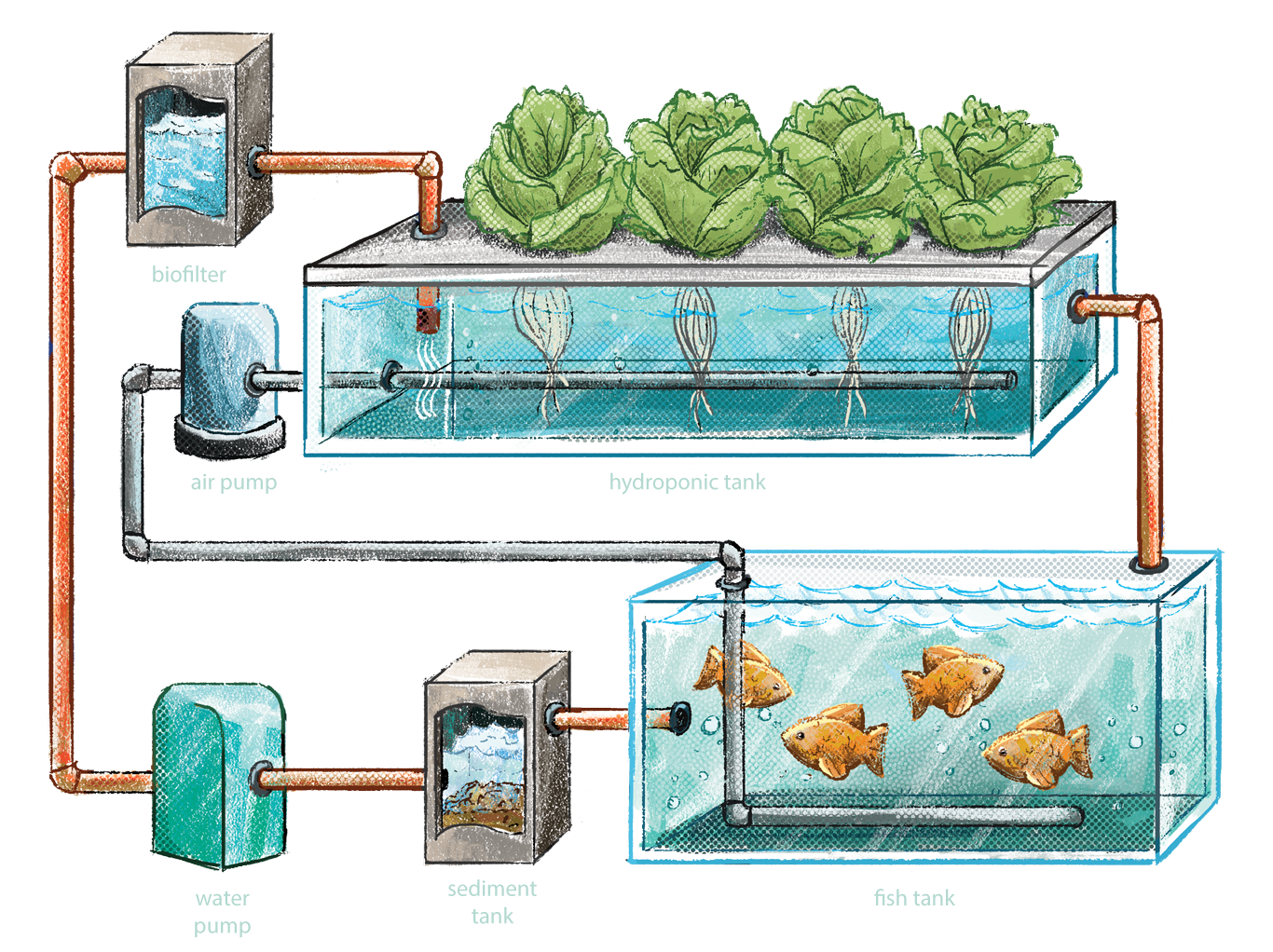
Hydroponic systems with fish, also known as aquaponics, combine aquaculture (the raising of fish) with hydroponics (the growing of plants in water). In aquaponics, the fish provide nutrients for the plants, and the plants help to clean the water for the fish.
Benefits of Hydroponic Systems with Fish
There are several benefits to using a hydroponic system with fish. These benefits include:
- Increased plant growth: The nutrients from the fish waste help to promote plant growth, resulting in larger and healthier plants.
- Reduced water usage: Hydroponic systems use less water than traditional soil-based gardening methods.
- No need for fertilizers: The fish waste provides all the nutrients that the plants need, so there is no need to add additional fertilizers.
- Pest and disease resistance: Hydroponic systems are less susceptible to pests and diseases than soil-based gardening methods.
Drawbacks of Hydroponic Systems with Fish
There are also some drawbacks to using a hydroponic system with fish. These drawbacks include:
- Initial cost: Hydroponic systems with fish can be more expensive to set up than traditional soil-based gardening methods.
- Maintenance: Hydroponic systems with fish require more maintenance than traditional soil-based gardening methods.
li>Space requirements: Hydroponic systems with fish require more space than traditional soil-based gardening methods.
Components of a Hydroponic System with Fish
A hydroponic system with fish, also known as aquaponics, combines fish farming with hydroponics to create a mutually beneficial ecosystem. The system consists of several essential components that work together to provide a thriving environment for both plants and fish.
Grow Beds
Grow beds are the containers where plants are grown in a hydroponic system. They can be made from a variety of materials, such as plastic, metal, or wood. Grow beds provide support for the plants and hold the nutrient-rich water solution that the plants absorb.
Nutrient Solution
The nutrient solution is the water-based solution that provides plants with the essential nutrients they need to grow. It contains a balanced blend of macronutrients (nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium) and micronutrients (iron, manganese, and zinc).
Fish Tank
The fish tank is where the fish are kept. It is important to choose a fish tank that is the appropriate size for the number of fish you plan to keep. The fish tank should also have a good filtration system to keep the water clean.
Water Pump
The water pump is used to circulate the water between the fish tank and the grow beds. The pump ensures that the water is constantly moving, which helps to keep the water oxygenated and prevents the build-up of waste products.
Aerator
The aerator is used to add oxygen to the water. This is important for both the fish and the plants. Fish need oxygen to breathe, and plants need oxygen to absorb nutrients.
Types of Hydroponic Systems with Fish
Hydroponic systems with fish can be classified into different types based on the method used to deliver nutrients to the plants. Each type has its own advantages and disadvantages, and the choice of system will depend on the specific needs of the grower.
Nutrient Film Technique (NFT)
The Nutrient Film Technique (NFT) is a hydroponic system that uses a thin film of nutrient-rich water to deliver nutrients to the plants. The water is pumped from a reservoir to the top of the grow bed, and then it flows down the bed, past the roots of the plants.
The water is then returned to the reservoir, and the cycle is repeated.NFT systems are relatively simple to set up and operate, and they can be used to grow a wide variety of plants. However, NFT systems can be prone to clogging, and they require a constant supply of nutrient-rich water.
Deep Water Culture (DWC)
Deep Water Culture (DWC) is a hydroponic system that grows plants in a deep reservoir of nutrient-rich water. The plants are suspended in the water, and their roots are constantly submerged. DWC systems are simple to set up and operate, and they can be used to grow a wide variety of plants.
However, DWC systems can be prone to root rot, and they require a constant supply of nutrient-rich water.
Ebb and Flow
Ebb and Flow hydroponic systems use a timer to flood the grow bed with nutrient-rich water and then drain it away. The cycle is repeated several times a day. Ebb and Flow systems are relatively simple to set up and operate, and they can be used to grow a wide variety of plants.
However, Ebb and Flow systems can be prone to clogging, and they require a constant supply of nutrient-rich water.
Aeroponics
Aeroponic systems grow plants in a mist of nutrient-rich water. The roots of the plants are suspended in the air, and they are constantly misted with water. Aeroponic systems are very efficient at delivering nutrients to the plants, and they can be used to grow a wide variety of plants.
However, Aeroponic systems are more complex to set up and operate than other hydroponic systems, and they require a constant supply of nutrient-rich water.
Fish Species for Hydroponic Systems
In a hydroponic system with fish, the selection of fish species is crucial. Different fish species have varying requirements and can impact the overall performance of the system. The following are some common types of fish suitable for hydroponic systems:
Tilapia
- Tilapia is a warm-water fish that is known for its fast growth rate and tolerance to high stocking densities.
- It is a popular choice for commercial hydroponic systems due to its adaptability and high yield potential.
- Tilapia can consume a wide range of feed, including algae, aquatic plants, and commercial fish feed.
Catfish
- Catfish are bottom-dwelling fish that are known for their ability to withstand poor water quality.
- They are omnivorous and can consume a variety of feed, including insects, worms, and commercial fish feed.
- Catfish can be raised in both indoor and outdoor hydroponic systems, and they can tolerate a wide range of temperatures.
Goldfish
- Goldfish are a popular choice for small-scale hydroponic systems.
- They are hardy fish that can tolerate a wide range of water conditions.
- Goldfish are omnivorous and can consume a variety of feed, including algae, aquatic plants, and commercial fish feed.
Koi
- Koi are a type of ornamental carp that is known for its beautiful coloration.
- They are relatively large fish that require a larger hydroponic system.
- Koi are omnivorous and can consume a variety of feed, including algae, aquatic plants, and commercial fish feed.
Plant Species for Hydroponic Systems with Fish
In a hydroponic system with fish, choosing the right plant species is crucial for the overall success of the system. Different plants have varying nutrient requirements, growth rates, and environmental preferences. Here’s a table listing some of the most commonly grown plant species in aquaponic systems:
| Plant Species | Nutritional Value | Growth Rate | Environmental Preferences |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lettuce | High in vitamins A, C, and K | Fast | Prefers cool temperatures and moderate light |
| Tomatoes | Excellent source of vitamin C and lycopene | Moderate | Requires warm temperatures and ample sunlight |
| Basil | Rich in antioxidants and essential oils | Fast | Prefers warm temperatures and bright light |
| Peppers | Good source of vitamins A and C, as well as capsaicin | Moderate | Needs warm temperatures and plenty of sunlight |
| Cucumbers | High in water content and electrolytes | Fast | Prefers warm temperatures and high humidity |
Management of Hydroponic Systems with Fish
Maintaining the health and productivity of a hydroponic system with fish requires careful management. This includes monitoring water quality, feeding the fish, and harvesting the plants.
Monitoring Water Quality
Water quality is critical for the health of both the fish and the plants. The following parameters should be monitored regularly:
- pH:The pH of the water should be maintained between 6.5 and 7.5.
- Ammonia:Ammonia is toxic to fish and plants. The ammonia level should be kept below 1 ppm.
- Nitrite:Nitrite is also toxic to fish and plants. The nitrite level should be kept below 0.5 ppm.
- Nitrate:Nitrate is a form of nitrogen that is essential for plant growth. The nitrate level should be maintained between 5 and 20 ppm.
- Dissolved oxygen:Dissolved oxygen is essential for the respiration of fish and plants. The dissolved oxygen level should be maintained above 5 ppm.
Feeding the Fish
The fish in a hydroponic system should be fed a high-quality diet that is appropriate for their species. The amount of food fed should be based on the number of fish, their size, and the water temperature.
Harvesting the Plants
The plants in a hydroponic system can be harvested when they reach maturity. The harvesting method will vary depending on the type of plant.
Advantages of Hydroponic Systems with Fish: Hydroponic System With Fish
Hydroponic systems with fish offer numerous advantages compared to traditional farming methods. These benefits include increased plant growth rates, reduced water usage, decreased fertilizer costs, and enhanced fish production.
Increased Plant Growth Rates
In a hydroponic system with fish, the water is naturally fertilized by the fish waste. This provides a constant supply of nutrients to the plants, leading to faster growth rates and higher yields. Additionally, the fish waste contains growth hormones that further stimulate plant development.
Reduced Water Usage, Hydroponic system with fish
Hydroponic systems use significantly less water than traditional soil-based farming methods. The water is recirculated and reused within the system, reducing water consumption by up to 90%. This makes hydroponic systems an attractive option for areas with limited water resources.
Reduced Fertilizer Costs
As the fish waste provides the necessary nutrients for plant growth, the need for additional fertilizers is minimized. This can result in significant cost savings for farmers, particularly those who rely on expensive synthetic fertilizers.
Increased Fish Production
The nutrient-rich water in a hydroponic system provides an ideal environment for fish growth. The fish benefit from the constant supply of food from the plant roots and the oxygenated water. As a result, fish production can be increased compared to traditional aquaculture methods.
Challenges of Hydroponic Systems with Fish
Hydroponic systems with fish offer numerous benefits, but they also come with certain challenges that need to be carefully managed to ensure the health of the fish and plants. These challenges include disease management, water quality management, and nutrient management.
Disease Management
One of the primary challenges in hydroponic systems with fish is disease management. The close proximity of fish and plants can increase the risk of disease transmission. Fish can carry diseases that can be harmful to plants, and vice versa.
It is important to implement proper disease prevention and control measures, such as regular monitoring of fish and plant health, quarantine of new fish, and use of disease-resistant plant varieties.
Hydroponic systems with fish, also known as aquaponics, offer a sustainable and efficient way to produce both fish and plants. By combining the benefits of aquaculture and hydroponics, these systems create a symbiotic relationship where the fish provide nutrients for the plants, while the plants filter the water for the fish.
To learn more about the benefits and techniques involved in setting up a hydroponic fish farm, visit our comprehensive guide at hydroponic fish farm . With proper planning and maintenance, hydroponic systems with fish can provide a reliable source of fresh, healthy food for your family and community.
Water Quality Management
Water quality is crucial for the health of both fish and plants in a hydroponic system. The water must be clean, well-oxygenated, and free of harmful chemicals. Fish produce waste that can accumulate in the water, and plants can release compounds that can affect water quality.
Regular water testing and maintenance, including filtration, aeration, and water changes, are essential to maintain optimal water quality.
Nutrient Management
Nutrient management is another important challenge in hydroponic systems with fish. Fish waste provides a natural source of nutrients for plants, but it is important to monitor nutrient levels and supplement as needed to ensure that both fish and plants receive the necessary nutrients.
Overfeeding fish or inadequate nutrient supplementation can lead to nutrient imbalances, which can negatively affect the health of the system.
Case Studies of Hydroponic Systems with Fish
Hydroponic systems with fish have gained popularity due to their sustainability and efficiency. Several successful case studies demonstrate the benefits of these systems.
The Green Revolution in Kenya
In Kenya, a hydroponic system with fish has transformed agriculture in rural areas. The system provides a reliable source of income for farmers and improves nutrition in communities. Fish waste provides nutrients for plants, reducing the need for chemical fertilizers.
The system has also created employment opportunities and improved access to fresh produce.
The Urban Farm in New York City
Gotham Greens, an urban farm in New York City, uses hydroponics with fish to produce leafy greens year-round. The system maximizes space and water usage, making it suitable for urban environments. The farm supplies fresh produce to local markets and restaurants, promoting sustainability and reducing transportation costs.
Conclusion
/GettyImages-142873284-7afec7706c2a4997841bde2792c7ff6b.jpg)
Hydroponic systems with fish offer a sustainable and efficient way to produce food. They combine the benefits of hydroponics and aquaculture, allowing for the production of both plants and fish in a controlled environment. This article has provided a comprehensive overview of hydroponic systems with fish, including their components, types, fish and plant species, management practices, advantages, challenges, and case studies.
Future of Hydroponic Systems with Fish
The future of hydroponic systems with fish looks promising. As the demand for sustainable and efficient food production methods continues to grow, these systems are expected to become increasingly popular. Advancements in technology and research will further improve the efficiency and productivity of these systems, making them even more attractive to commercial and home growers alike.
Epilogue
As we conclude our exploration of hydroponic systems with fish, let us remember the potential they hold for sustainable and efficient food production. Embracing this innovative approach empowers us to nourish our communities while respecting the delicate balance of our planet.
May this guide serve as a beacon of knowledge, inspiring you to create thriving and resilient ecosystems that seamlessly integrate plants and fish.
Question & Answer Hub
What are the key benefits of a hydroponic system with fish?
Hydroponic systems with fish offer numerous benefits, including increased plant growth rates, reduced water usage, reduced fertilizer costs, and increased fish production.
What are the different types of fish that can be raised in a hydroponic system?
Various types of fish can be raised in a hydroponic system, including tilapia, catfish, goldfish, and koi.
How do I manage water quality in a hydroponic system with fish?
Water quality management in a hydroponic system with fish involves monitoring pH levels, dissolved oxygen levels, and nutrient concentrations, and making adjustments as needed.
