Dizzy symptoms causes are a topic that often sparks curiosity and concern. This article will delve into the underlying causes of dizziness, exploring the various factors that can trigger this common yet unsettling sensation.
Dizziness can manifest in different forms, from mild lightheadedness to severe vertigo. Understanding the root cause of dizziness is crucial for effective management and treatment.
Causes of Dizziness: Dizzy Symptoms Causes
Dizziness is a common symptom that can be caused by a variety of factors. Some of the most common causes include:
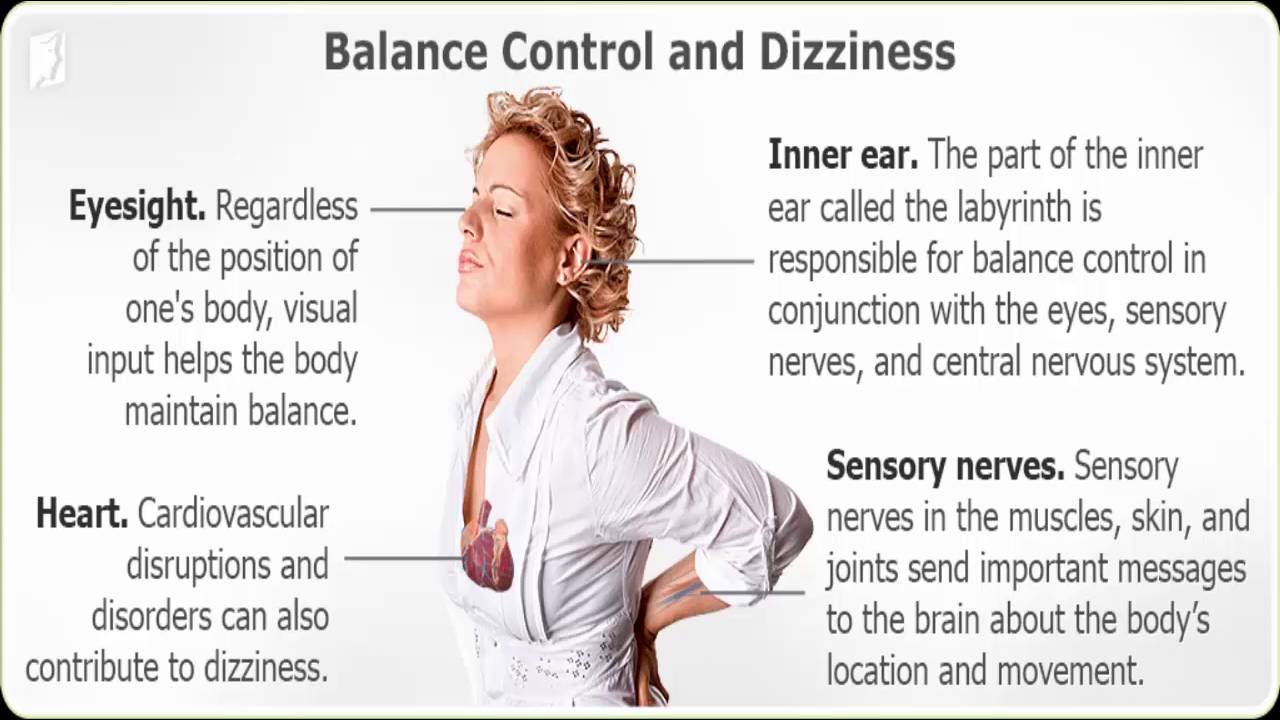
- Inner ear issues:The inner ear is responsible for balance, so any problems with this area can lead to dizziness. This can be caused by infections, such as labyrinthitis or vestibular neuritis, or by a condition called benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV).
- Blood pressure changes:Sudden changes in blood pressure can also cause dizziness. This can be caused by dehydration, anemia, or certain medications.
- Dehydration:Dehydration can lead to dizziness because it can cause a decrease in blood volume. This can make it difficult for the heart to pump blood to the brain, which can lead to dizziness.
- Medications:Certain medications, such as antibiotics, antidepressants, and blood pressure medications, can cause dizziness as a side effect.
- Infections:Infections, such as the flu or a sinus infection, can also cause dizziness. This is because the infection can cause inflammation in the inner ear or other parts of the body that are involved in balance.
- Neurological conditions:Certain neurological conditions, such as multiple sclerosis or Parkinson’s disease, can also cause dizziness. This is because these conditions can damage the nerves that are involved in balance.
Dizzy symptoms can have a range of causes, from dehydration to certain medical conditions. If you’re experiencing dizziness, it’s important to consult a doctor to determine the underlying cause. One common cause of dizziness is vertigo, which is a sensation of spinning or tilting.
To learn more about the specific causes of vertigo dizziness, visit this informative article: what causes vertigo dizziness . This article provides a comprehensive overview of the various factors that can contribute to vertigo symptoms.
Types of Dizziness

Dizziness encompasses a range of sensations that can be described as lightheadedness, unsteadiness, or a spinning sensation. These sensations arise from disturbances in the vestibular system, which is responsible for balance and spatial orientation.
There are several types of dizziness, each with its unique characteristics and underlying mechanisms:
Vertigo, Dizzy symptoms causes
- A false sense of spinning or whirling, either of oneself or the surroundings.
- Often caused by disturbances in the inner ear or brainstem, which are responsible for balance.
- Examples: Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV), Ménière’s disease, vestibular neuritis.
Lightheadedness
- A sensation of faintness or near-fainting.
- Caused by a temporary drop in blood pressure or blood flow to the brain.
- Examples: Orthostatic hypotension (dizziness upon standing), vasovagal syncope (fainting due to emotional triggers or dehydration).
Presyncope
- A feeling of impending fainting or loss of consciousness.
- Caused by a significant drop in blood pressure or blood flow to the brain.
- Examples: Cardiac arrhythmias, severe dehydration, blood loss.
Symptoms Associated with Dizziness
Dizziness is often accompanied by other symptoms that can provide clues about the underlying cause. These symptoms may include:
- Nausea and vomiting: These symptoms are common in people with dizziness caused by motion sickness, inner ear problems, or certain medications.
- Difficulty concentrating: This symptom can be caused by dizziness related to anxiety, depression, or certain neurological conditions.
- Headaches: Headaches can accompany dizziness caused by migraines, high blood pressure, or certain medications.
- Vision changes: Blurred vision, double vision, or other vision changes can occur with dizziness caused by eye problems, neurological conditions, or certain medications.
- Hearing loss: Hearing loss or ringing in the ears can be associated with dizziness caused by inner ear problems or certain medications.
- Numbness or tingling: Numbness or tingling in the arms, legs, or face can occur with dizziness caused by neurological conditions or certain medications.
- Weakness or fatigue: Weakness or fatigue can accompany dizziness caused by anemia, dehydration, or certain medications.
The presence of these symptoms along with dizziness can help your doctor determine the underlying cause and recommend appropriate treatment.
Risk Factors for Dizziness

Dizziness can affect people of all ages and backgrounds. However, certain risk factors increase the likelihood of experiencing dizziness. These include:
- Age:As people age, their balance systems become less effective, making them more susceptible to dizziness.
- Certain medical conditions:Conditions that affect the inner ear, such as Ménière’s disease, can cause dizziness. Other medical conditions, such as heart disease, diabetes, and high blood pressure, can also contribute to dizziness.
- Lifestyle habits:Certain lifestyle habits, such as smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and poor sleep habits, can increase the risk of dizziness.
Diagnosis of Dizziness
Diagnosing dizziness involves a thorough evaluation to determine the underlying cause. The process includes:
Physical Examination
- Observation of gait, balance, and posture
- Assessment of eye movements (nystagmus)
- Head and neck examination for tenderness or abnormalities
- Neurological examination (reflexes, sensation, coordination)
Medical History Review
- Symptoms onset, duration, and severity
- Associated symptoms (e.g., hearing loss, nausea, vomiting)
- Medical history (e.g., ear infections, head trauma)
- Medications and lifestyle factors
Diagnostic Tests
- Vestibular function tests:Assess the function of the inner ear and vestibular nerve
- Audiometry:Evaluates hearing function
- Electrocardiogram (ECG):Checks for heart rhythm abnormalities
- Imaging techniques:
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI):Provides detailed images of the brain and inner ear
- Computed tomography (CT) scan:Useful for detecting structural abnormalities in the brain and inner ear
Treatment Options for Dizziness
Treatment for dizziness depends on the underlying cause. The goal of treatment is to alleviate symptoms and prevent further episodes.
Medications can be used to treat dizziness caused by certain conditions, such as motion sickness, vertigo, and Meniere’s disease. These medications may include antihistamines, anticholinergics, and benzodiazepines.
Physical therapy can be helpful for dizziness caused by balance disorders. Exercises can help to improve balance and coordination.
Lifestyle modifications can also help to reduce dizziness. These modifications may include:
- Avoiding triggers that cause dizziness
- Getting regular exercise
- Eating a healthy diet
- Getting enough sleep
- Managing stress
Last Recap
In conclusion, the causes of dizziness are multifaceted, ranging from benign conditions to more serious underlying health issues. Seeking medical attention is essential for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan. By understanding the potential causes of dizziness, we can take proactive steps to manage and alleviate this common symptom.
