Commercial aquaponics systems design is a fascinating field that combines the principles of aquaculture and hydroponics to create sustainable and profitable food production systems. This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of commercial aquaponics systems design, providing valuable insights and practical guidance for aspiring aquapreneurs.
From understanding the fundamental principles of system design to selecting the right species and managing the system effectively, this guide will equip you with the knowledge and skills necessary to establish a thriving commercial aquaponics operation.
System Design

Designing commercial aquaponics systems involves careful consideration of various factors to ensure optimal performance and profitability. Understanding the fundamental principles of system design is crucial for creating efficient and sustainable operations.
System Design Principles
The design of commercial aquaponics systems should adhere to the following principles:
- Maximize Water Usage:Efficient water management is essential to minimize water consumption and optimize nutrient availability for plants.
- Balance Nutrient Cycling:The system should be designed to maintain a balanced nutrient cycle between the fish and plants, ensuring optimal growth and productivity.
- Optimize Oxygenation:Adequate oxygenation is crucial for both fish and plant health. The system should provide sufficient aeration and water flow to maintain dissolved oxygen levels.
- Control Temperature:Temperature is a critical factor affecting fish and plant growth. The system should be designed to maintain optimal temperature ranges through insulation, heating, or cooling mechanisms.
System Design Examples
There are various system designs used in commercial aquaponics, each with its advantages and disadvantages:
- Recirculating Aquaculture System (RAS):RAS involves recirculating water between the fish tanks and grow beds, minimizing water usage and nutrient loss.
- Nutrient Film Technique (NFT):NFT systems use shallow, sloping channels where nutrient-rich water flows over the roots of plants.
- Deep Water Culture (DWC):DWC systems suspend plants in nutrient-rich water, providing constant access to nutrients and oxygen.
Water Quality Management and Filtration
Maintaining optimal water quality is crucial for the health and productivity of both fish and plants in aquaponics systems. Water filtration plays a vital role in removing solids, pathogens, and other contaminants from the water.
- Mechanical Filtration:Removes solid particles using screens, filters, or settling tanks.
- Biological Filtration:Uses beneficial bacteria to break down organic matter and convert ammonia into less toxic forms.
- Chemical Filtration:Employs activated carbon or other chemicals to remove specific contaminants or adjust pH levels.
Species Selection
Selecting the right fish and plant species is crucial for the success of commercial aquaponics systems. Factors to consider include growth rates, nutritional value, market demand, and compatibility with the system’s environment.
Fish Species
Commonly used fish species in commercial aquaponics include:
- Tilapia: Fast-growing, tolerant of high densities, and in high demand.
- Catfish: Bottom-feeders that utilize waste nutrients, have a good feed conversion ratio, and are in demand for their meat.
- Salmon: High-value fish with a high nutritional profile, but require more specialized systems.
Plant Species
Suitable plant species for commercial aquaponics include:
- Lettuce: Fast-growing leafy greens with high market demand.
- Basil: A popular herb with a high essential oil content and market value.
- Tomatoes: A high-value fruit crop with a long growing season.
Crop Rotation and Companion Planting
Crop rotation and companion planting are important practices in commercial aquaponics systems to:
- Prevent disease and pest buildup.
- Maximize nutrient uptake by different plant species.
- Improve soil health and water quality.
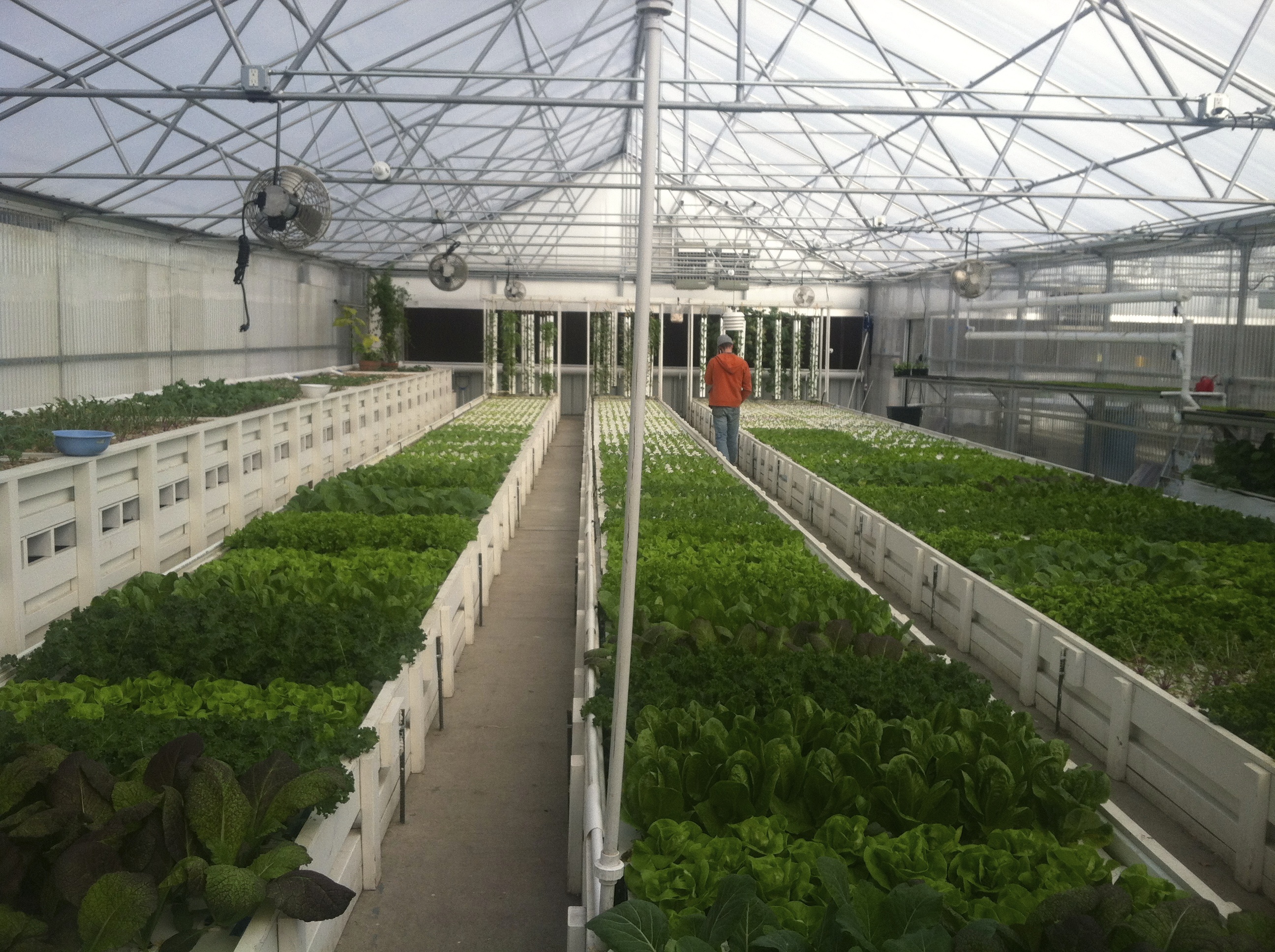
System Management
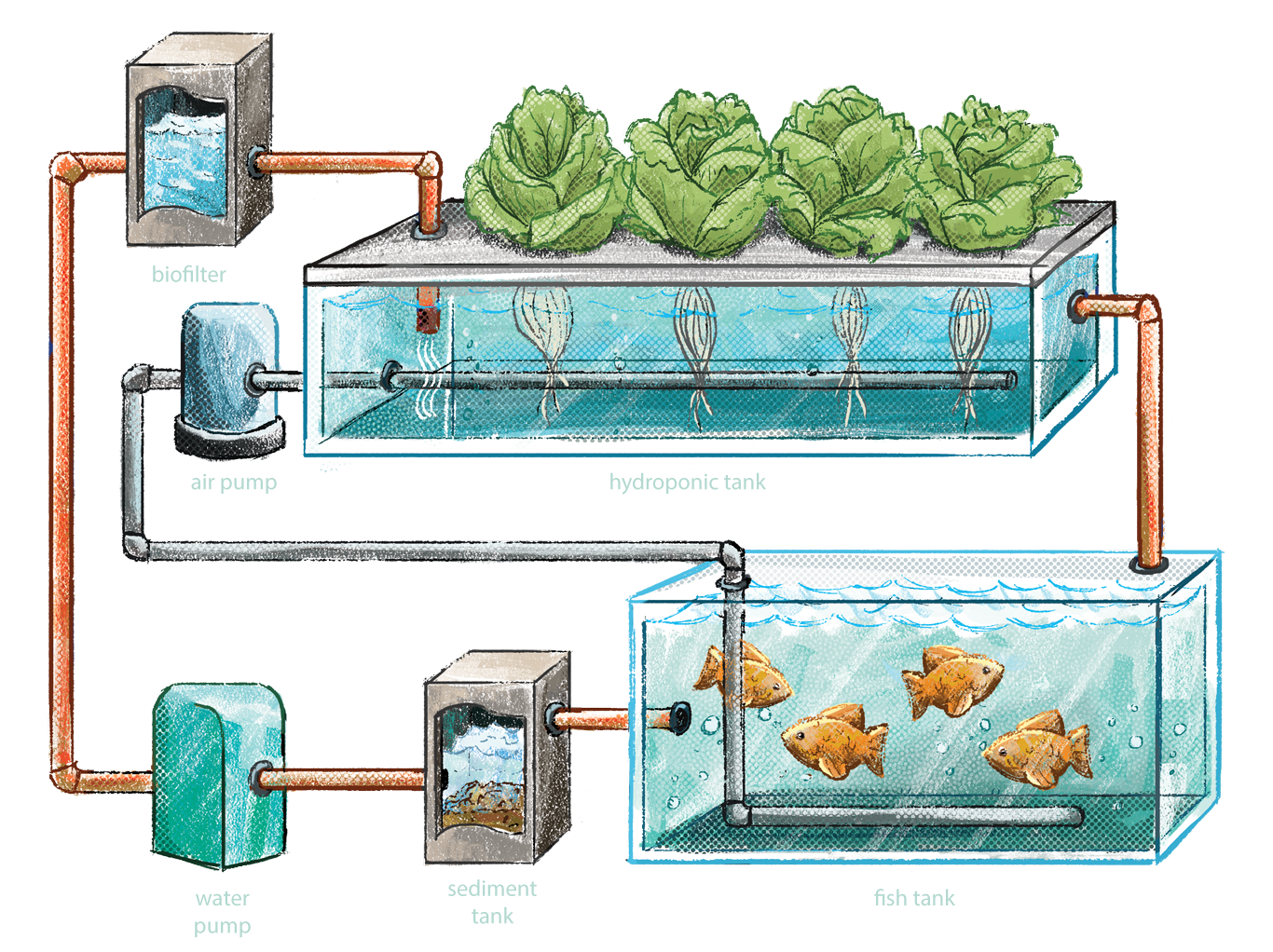
System management in commercial aquaponics systems is crucial to ensure optimal performance and prevent potential problems. It involves monitoring and controlling key operational parameters, performing routine maintenance, and keeping accurate records for analysis and troubleshooting.
Key Operational Parameters
The following key operational parameters should be closely monitored and controlled in commercial aquaponics systems:
- Water temperature:Ideal temperature ranges vary depending on the species being cultivated, but generally, most aquatic organisms thrive within a range of 18-28°C (64-82°F).
- pH:The pH level of the water should be maintained within a narrow range, typically between 6.5 and 7.5, to ensure optimal nutrient uptake by plants and fish health.
- Dissolved oxygen levels:Adequate dissolved oxygen levels are essential for the respiration of fish and beneficial bacteria. Optimal levels vary depending on the species, but generally, they should be maintained above 5 mg/L.
Economic Considerations

Economic factors play a crucial role in determining the profitability of commercial aquaponics systems. Understanding these factors is essential for making informed decisions about system design and operation.
Key economic factors to consider include:
- Production costs: These include expenses related to infrastructure, equipment, seed, feed, energy, and labor.
- Market demand: Identifying and targeting markets with strong demand for aquaponics products is crucial for ensuring profitability.
- Labor requirements: The labor required for system maintenance, harvesting, and marketing should be carefully considered.
Economic Viability of Different System Designs
The economic viability of commercial aquaponics systems can vary depending on the system design. The following table compares the key economic factors for different system designs:
| System Design | Production Costs | Market Demand | Labor Requirements ||—|—|—|—|| Recirculating Aquaculture System (RAS) | High | Moderate | High || Nutrient Film Technique (NFT) | Moderate | High | Low || Deep Water Culture (DWC) | Low | Moderate | Low || Media-Based Aquaponics | Moderate | Moderate | Moderate |
Government Incentives and Support
Government incentives and support can play a significant role in promoting the development of commercial aquaponics systems. These may include:
- Grants and subsidies for capital investments
- Tax incentives for energy-efficient systems
- Technical assistance and training programs
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Commercial aquaponics systems offer significant environmental benefits, contributing to a more sustainable food production approach.
Aquaponics systems conserve water resources by recirculating water within the system. This reduces water consumption compared to traditional agriculture, which often relies on extensive irrigation.
Reduced Chemical Use
Aquaponics systems minimize the need for chemical fertilizers and pesticides. The fish waste provides natural nutrients for the plants, reducing the reliance on synthetic inputs.
Waste Reduction
Aquaponics systems promote waste reduction by utilizing fish waste as a valuable resource for plant growth. This reduces the environmental impact associated with disposal of fish waste and contributes to a more circular food production system.
Challenges and Opportunities
While commercial aquaponics systems offer environmental benefits, there are also challenges to consider:
- Energy consumption: Aquaponics systems require energy for water filtration, aeration, and lighting.
- Disease management: Maintaining healthy fish populations is crucial to prevent disease outbreaks that can impact both fish and plants.
Opportunities for reducing the environmental footprint of commercial aquaponics systems include:
- Utilizing renewable energy sources, such as solar or wind power, to reduce energy consumption.
- Implementing biosecurity measures to minimize the risk of disease outbreaks.
- Exploring innovative technologies to improve water filtration and aeration efficiency.
Best Practices
Sustainable commercial aquaponics system design and operation incorporate best practices such as:
- Selecting energy-efficient equipment and utilizing renewable energy sources.
- Implementing a comprehensive disease management plan to prevent outbreaks.
- Optimizing water filtration and aeration systems to minimize energy consumption.
- Utilizing organic waste streams, such as compost, to supplement fish waste as a nutrient source.
Future Trends and Innovations

The future of commercial aquaponics systems is bright, with emerging trends and innovations promising to revolutionize the industry and contribute significantly to global food security and sustainability.
Commercial aquaponics systems design requires careful consideration of factors such as water quality, nutrient availability, and fish stocking density. For more information on hydroponic systems in Hamilton, visit hydroponics hamilton . By integrating these principles, aquaponics systems can provide sustainable and efficient food production.
One key trend is the increasing adoption of automation and artificial intelligence (AI) in aquaponics systems. Automation can streamline tasks such as water quality monitoring, feeding, and harvesting, reducing labor costs and improving efficiency. AI can analyze data from sensors and make real-time adjustments to optimize system performance, leading to increased yields and reduced waste.
Vertical Farming
Another significant trend is the integration of aquaponics with vertical farming, where plants are grown in vertically stacked layers within a controlled environment. This combination allows for higher crop yields per square foot, making it a viable option for urban areas with limited land space.
Vertical farming also enables year-round production, regardless of outdoor climate conditions.
Global Food Security and Sustainability
Commercial aquaponics systems have the potential to make a substantial contribution to global food security and sustainability. By combining fish and plant production in a closed-loop system, aquaponics can provide a reliable source of fresh, nutritious food while minimizing environmental impact.
Aquaponics systems use less water than traditional agriculture and can be located in urban areas, reducing transportation costs and emissions. They also eliminate the need for chemical fertilizers and pesticides, making them an environmentally friendly alternative to conventional farming practices.
Vision for the Future, Commercial aquaponics systems design
The future of commercial aquaponics systems holds immense promise for transforming the food production industry. As technology continues to advance and innovation thrives, aquaponics will become increasingly efficient, sustainable, and accessible.
In the years to come, we can envision large-scale aquaponics facilities operating in urban centers, providing fresh, local food to growing populations while promoting environmental stewardship. Aquaponics has the potential to revolutionize the way we produce food, ensuring a secure and sustainable future for generations to come.
Last Recap: Commercial Aquaponics Systems Design
/GettyImages-142873284-7afec7706c2a4997841bde2792c7ff6b.jpg)
In conclusion, commercial aquaponics systems design offers a promising solution to the challenges of global food security and sustainability. By embracing innovative technologies and best practices, we can harness the power of aquaponics to create a more resilient and sustainable food system for the future.
Key Questions Answered
What are the key factors to consider when designing a commercial aquaponics system?
The key factors to consider include water quality management, filtration, system size and capacity, species selection, and economic viability.
How do I select the right fish and plant species for my commercial aquaponics system?
Consider factors such as growth rates, nutritional value, market demand, and compatibility with the system design.
What are the key operational parameters that need to be monitored and controlled in a commercial aquaponics system?
Monitor and control water temperature, pH, dissolved oxygen levels, nutrient levels, and fish health.
